

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Rate of Radioactive Decay
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
1-9-2020
2229
Rate of Radioactive Decay
During natural radioactive decay, not all atoms of an element are instantaneously changed to atoms of another element. The decay process takes time and there is value in being able to express the rate at which a process occurs. A useful concept is half-life, which is the time required for half of the starting material to change or decay. Half-lives can be calculated from measurements on the change in mass of a nuclide and the time it takes to occur. The only thing we know is that in the time of that substance's half-life, half of the original nuclei will disintegrate. Although chemical changes were sped up or slowed down by changing factors such as temperature, concentration, etc, these factors have no effect on half-life. Each radioactive isotope will have its own unique half-life that is independent of any of these factors.
The half-lives of many radioactive isotopes have been determined and they have been found to range from extremely long half-lives of 10 billion years to extremely short half-lives of fractions of a second.
|
Table 1: Table of Selected Half-lives |
|||||
|
Element |
Mass Number (A) |
Half-life |
Element |
Mass Number (A) |
Half Life |
|
Uranium |
238 |
4.5 Billion years |
Californium |
251 |
800 years |
|
Neptunium |
240 |
1 hour |
Nobelium |
254 |
3 seconds |
|
Plutonium |
243 |
5 hours |
Carbon |
14 |
5730 years |
|
Americium |
245 |
25 minutes |
Carbon |
16 |
740 milliseconds |
The quantity of radioactive nuclei at any given time will decrease to half as much in one half-life. For example, if there were 100g of Cf-251 in a sample at some time, after 800 years, there would be 50g of Cf-251 remaining and after another 800 years (1600 years total), there would only be 25g
remaining.
Remember, the half-life is the time it takes for half of your sample, no matter how much you have, to remain. Each half-life will follow the same general pattern as Cf
-251. The only difference is the length of time it takes for half of a sample to decay.
Example 1
Using the graph, what is the half-life of an isotope that produces the following graph of decay over time:
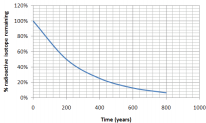
Solution
We know that the half-life is the time it takes for half of a sample to change. How long did it take for half of our isotope to change? It took approximately 200 years for 100% of our sample to leave only 50% (half of the original amount) remaining. The half-life is 200 years.
*Notice that after another 200 years (400 years total), 25% remains (half of 50%)
Look carefully at the graph in the previous example. All types of radioactive decay make a graph of the same general shape. The only difference is the scale and units of the x -axis, as the half-life time will be different.
Example 2
If there are 60 grams of Np -240 present, how much Np-240 will remain after 4 hours? (Np -240 has a half-life of 1 hour)
Solution
Np -240 with a half life of only 1 hour.
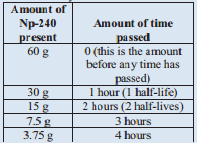
After 4 hours, only 3.75g of our original 60g sample would remain the radioactive isotope Np -240.
Example 3
A sample of Ac -225 originally contained 80 grams and after 50 days only 2.55 grams of the original Ac-225 remain. What is the half life of Ac -225?
Solution
We are going to tackle this problem similar to the last problem. The difference is that we are looking for the half-life time. Let's set up a similar table, though:
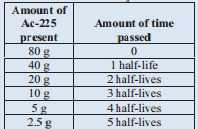
We know that 50 days is the same as 5 half-lives. Therefore, 1 half-life is 10 days. The half-life of Ac -225 is 10 days.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















