

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Effects of Long-term Radiation Exposure on the Human Body
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
4-9-2020
2303
Effects of Long-term Radiation Exposure on the Human Body
The effects of radiation depend on the type, energy, and location of the radiation source, and the length of exposure. As shown in Figure 1 , the average person is exposed to background radiation, including cosmic rays from the sun and radon from uranium in the ground (see the Chemistry in Everyday Life feature on Radon Exposure); radiation from medical exposure, including CAT scans, radioisotope tests, X-rays, and so on; and small amounts of radiation from other human activities, such as airplane flights (which are bombarded by increased numbers of cosmic rays in the upper atmosphere), radioactivity from consumer products, and a variety of radionuclides that enter our bodies when we breathe (for example, carbon-14) or through the food chain (for example, potassium-40, strontium-90, and iodine-131).
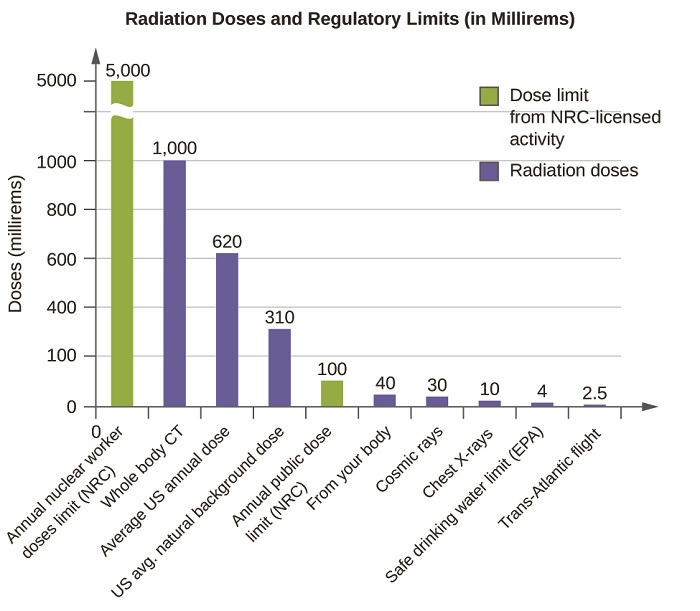
Figure 1 : The total annual radiation exposure for a person in the US is about 620 mrem. The various sources and their relative amounts are shown in this bar graph. (source: U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission).
A short-term, sudden dose of a large amount of radiation can cause a wide range of health effects, from changes in blood chemistry to death. Short-term exposure to tens of rems of radiation will likely cause very noticeable symptoms or illness; a dose of about 500 rems is estimated to have a 50% probability of causing the death of the victim within 30 days of exposure. Exposure to radioactive emissions has a cumulative effect on the body during a person’s lifetime, which is another reason why it is important to avoid any unnecessary exposure to radiation. Health effects of short-term exposure to radiation are shown in Table 1.
| Exposure (rem) | Health Effect | Time to Onset (without treatment) |
|---|---|---|
| 5–10 | changes in blood chemistry | — |
| 50 | nausea | hours |
| 55 | fatigue | — |
| 70 | vomiting | — |
| 75 | hair loss | 2–3 weeks |
| 90 | diarrhea | — |
| 100 | hemorrhage | — |
| 400 | possible death | within 2 months |
| 1000 | destruction of intestinal lining | — |
| internal bleeding | — | |
| death | 1–2 weeks | |
| 2000 | damage to central nervous system | — |
| loss of consciousness; | minutes | |
| death | hours to days |
It is impossible to avoid some exposure to ionizing radiation. We are constantly exposed to background radiation from a variety of natural sources, including cosmic radiation, rocks, medical procedures, consumer products, and even our own atoms. We can minimize our exposure by blocking or shielding the radiation, moving farther from the source, and limiting the time of exposure.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















