
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
GAMMA (γ) RAYS
المؤلف:
S. Gibilisco
المصدر:
Physics Demystified
الجزء والصفحة:
485
5-11-2020
2210
GAMMA (γ) RAYS
As the wavelength of EM rays becomes shorter and shorter, their penetrating power increases until focusing is impossible. The cutoff point where the x-ray region ends and the gamma-ray region begins is approximately 0.01 nm (10-11 m). Gamma rays can, in theory, get shorter than this without limit.
The gamma classification represents the most energetic of all EM fields. Short-wavelength gamma rays can penetrate several centimeters of solid lead or more than a meter of concrete. They are even more damaging to living tissue than x-rays. Gamma rays come from radioactive materials, both natural (such as radon) and human-made (such as plutonium).
Radiation counters are the primary means of detecting and observing sources of gamma rays. Gamma rays can dislodge particles from the nuclei of atoms they strike. These subatomic particles can be detected by a counter. One type of radiation counter consists of a thin wire strung within a sealed cylindrical metal tube filled with alcohol vapor and argon gas. When a highspeed subatomic particle enters the tube, the gas is ionized for a moment. A voltage is applied between the wire and the outer cylinder so that a pulse of electric current occurs whenever the gas is ionized. Such a pulse produces a click in the output of an amplifier connected to the device.
A simplified diagram of a radiation counter is shown in Fig. 1. A glass window with a metal sliding door is cut in the cylinder. The door can be opened to let in particles of low energy and closed to allow only the most energetic particles to get inside. High-speed subatomic particles, which are tiny yet massive for their size, have no trouble penetrating the window glass if they are moving fast enough. When the door is closed, gamma rays can penetrate it with ease.
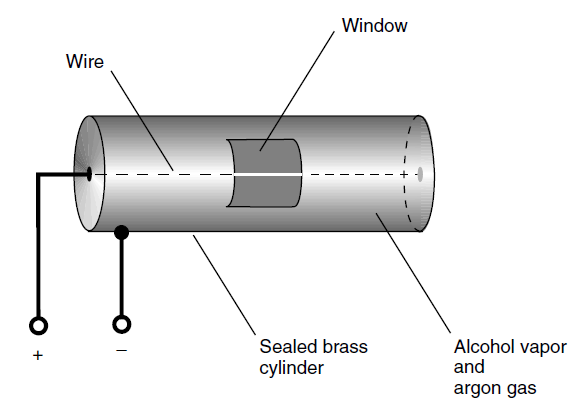
Fig. 1. Simplified diagram of a radiation counter.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكهرومغناطيسية
الاكثر قراءة في الكهرومغناطيسية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















