
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Negative Image Distance
المؤلف:
E. R. Huggins
المصدر:
Physics 2000
الجزء والصفحة:
1012
3-1-2021
2483
Negative Image Distance
The lens equation is more general than you might expect, for it works equally well for positive and negative distances and focal lengths. Let us start by seeing what we mean by a negative image distance.
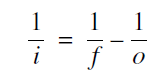 (1)
(1)
let us see what happens if 1/o is bigger than 1/f so that i turns out to be negative. If 1/o is bigger than 1/f, that means that o is less than f and we have placed the object within the focal length as shown in Figure (1). When we trace out two rays from the tip of the image, we find that the rays diverge after they pass through the lens. They diverge as if they were coming from a point behind the object, a point shown by the dotted lines. In this case we have what is called a virtual image, which is located at a negative image distance (i). This negative image distance is correctly given by the lens equation (1).
(We will not drag you through another geometrical proof of the lens equation for negative image distances. It should be fairly convincing that just when the image distance becomes negative in the lens equation, the geometry shows that we switch from a real image on the right side of the lens to a virtual image on the left.)

Figure 1: When the object is located within the focal length, we get a virtual image behind the object
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















