
Stability of Laser Resonators
 المؤلف:
Walter Koechner, Michael Bass
المؤلف:
Walter Koechner, Michael Bass
 المصدر:
Solid-State Lasers
المصدر:
Solid-State Lasers
 الجزء والصفحة:
160
الجزء والصفحة:
160
 20-1-2021
20-1-2021
 2005
2005
Stability of Laser Resonators
For certain combinations of R1, R2, and L, the equations summarized in the previous subsection give nonphysical solutions (that is, imaginary spot sizes). This is the region where low-loss modes do not exist in the resonator.
Light rays that bounce back and forth between the spherical mirrors of a laser resonator experience a periodic focusing action. The effect on the rays is the same as in a periodic sequence of lenses. Rays passing through a stable sequence of lenses are periodically refocused. For unstable systems the rays become more and more dispersed the further they pass through the sequence. In an optical resonator operated in the stable region, the waves propagate between reflectors without spreading appreciably. This fact can be expressed by a stability criterion
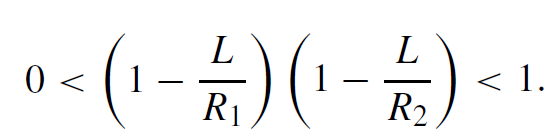 .......(1)
.......(1)
To show graphically which type of resonator is stable and which is unstable, it is useful to plot a stability diagram in which each particular resonator geometry is represented by a point. This is shown in Fig. 1, where the parameters
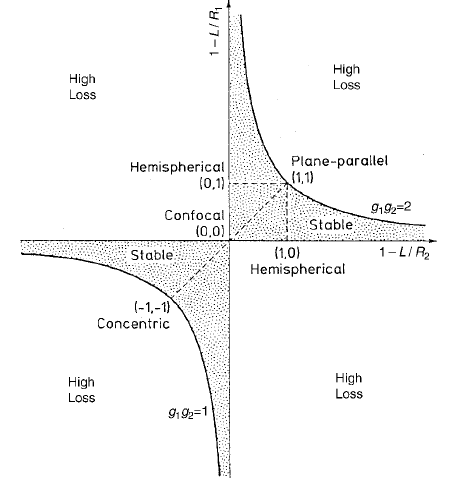
FIGURE 1. Stability diagram for the passive laser resonator.
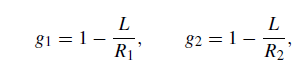 ...........(2)
...........(2)
are drawn as the coordinate axes.
All cavity configurations are unstable unless they correspond to points located in the area enclosed by a branch of the hyperbola g1g2 = 1 and the coordinate axes. The origin of the diagram represents the confocal system.
The resonators located along the dashed line, oriented at 45◦ with respect to the coordinate axis, are symmetric configurations, that is, they have mirrors with the same radius of curvature.
The diagram is divided into positive and negative branches defining quadrants for which g1g2 is either positive or negative. The reason for this classification becomes clear when we discuss unstable resonators.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


