

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Chronic Inflammation
المؤلف:
Bezabeh ,M. ; Tesfaye,A.; Ergicho, B.; Erke, M.; Mengistu, S. ; Bedane,A. and Desta, A
المصدر:
General Pathology
الجزء والصفحة:
25-2-2016
2350
Chronic Inflammation
Definition: Chronic inflammation can be defined as a prolonged inflammatory process (weeks or months) where an active inflammation, tissue destruction and attempts at repair are proceeding simultaneously.
Causes of chronic inflammation:
1. Persistent infections
- Certain microorganisms associated with intracellular infection such as tuberculosis,
leprosy, certain fungi etc characteristically cause chronic inflammation.
- These organisms are of low toxicity and evoke delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
2. Prolonged exposure to non-degradable but partially toxic substances either endogenous lipid components which result in atherosclerosis or exogenous substances such as silica, asbestos.
3. Progression from acute inflammation: Acute inflammation almost always progresses to chronic inflammation following:
a. Persistent suppuration as a result of uncollapsed abscess cavities, foreign body materials (dirt, cloth, wool, etc), sequesterum in osteomylitis, or a sinus/fistula from chronic abscesses.
4. Autoimmunity. Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosis are chronic inflammations from the outset.
Morphology:
Cells of chronic inflammation:
- Monocytes and Macrophages are the prima Dona (primary cells) in chronic inflammation. Macrophages arise from the common precursor cells in the bone marrow, which give rise to blood monocytes. These cells are then diffusely scattered in various parts of the body, in the liver (Kupffer cells), spleen, lymph nodes (sinus histiocytes), lungs (alviolar macrophages), bone marrow, brain (microglia), skin (Langerhan’s cells), etc…. These cells constitute the mononuclear- phagocytic system.
- Macrophages are scavenger cells of the body.
Other cells in chronic inflammation:
1. T-Lymphocytes are primarily involved in cellular immunity with lymphokine production, and they are the key regulator and effector cells of the immune system.
2. B-lymphocytes and Plasma cells produce antibody directed either against persistent antigen in the inflammatory site or against altered tissue components.
3. Mast cells and eosinophils appear predominantly in response to parasitic infestations & allergic reactions.
Though neutrophils are hallmarks of acute inflammatory reactions, large numbers of neutrophils may be seen in some forms of chronic inflammation, notably chronic osteomylitis, actinomycosis, & choric lung diseases induced by smoking and other stimuli.
Thus, the overall differentiation points between acute and chronic inflammations include:
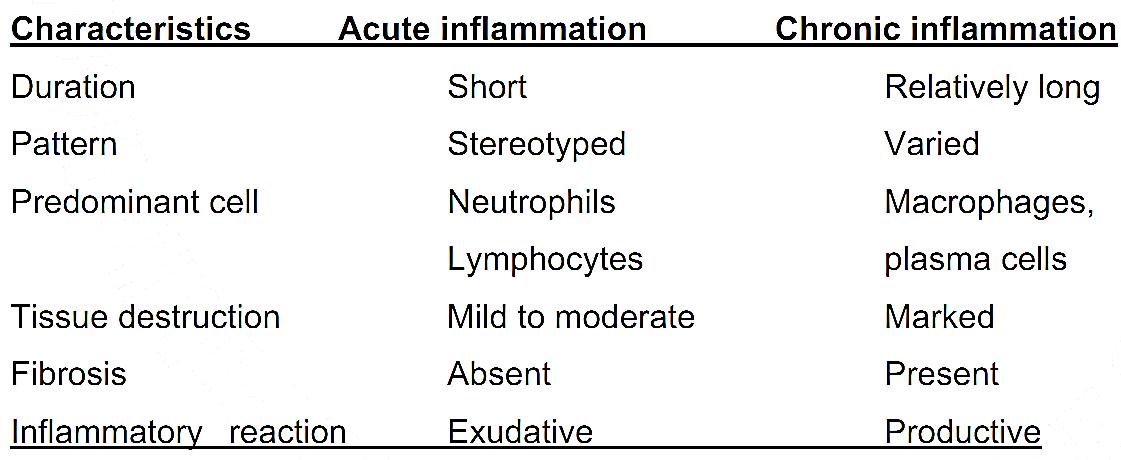
References
Bezabeh ,M. ; Tesfaye,A.; Ergicho, B.; Erke, M.; Mengistu, S. and Bedane,A.; Desta, A.(2004). General Pathology. Jimma University, Gondar University Haramaya University, Dedub University.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















