

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الحيوية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الحيوية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Central Vacuole
المؤلف:
AN INTRODUCTION TO PLANT BIOLOGY-1998
المصدر:
JAMES D. MAUSETH
الجزء والصفحة:
24-10-2016
3128
Central Vacuole
Within young, small cells are organelles, vacuoles, that have just a single membrane, the vacuole membrane, also called the tonoplast. Vacuoles often appear to be empty ( Fig ; Table ) because they store mostly water and salts that cannot be preserved for microscopy. However, they sometimes contain visible crystals, starch, protein bodies, and various types of granules or fibrous materials in addition to water and salts.
As a cell grows and enlarges, vacuoles expand and merge until there is just one large central vacuole. Because it contains primarily water and salts, the central vacuole can expand rapidly, forcing the cell to grow rapidly as well. Animal cells must synthesize complete protoplasm to grow, but plant cells need only increase the amount of vacuolar water. Over a long period, plants must produce additional proteins, membranes, and organelles or they would become almost pure water.
In addition to cell growth, the central vacuole functions in storage of both nutrient reserves and waste products. In seed cells, vacuoles may be filled with starch or protein that will be used when the seed germinates, perhaps 10 to 50 years after the material was deposited in the vacuole. Calcium regulates the activity of many enzymes, and plant cells keep protoplasmic calcium concentrations at the proper level by moving calcium into the vacuole, where it reacts with oxalic acid and crystallizes into an inert form. Other nutrients such as potassium may move in and out of the vacuole on a daily basis. The water-soluble pigments in many flowers, fruits, and red beets occur in vacuoles as well.
Table : Concentrations of nutients in vacuoles isolated from barley leaf cell
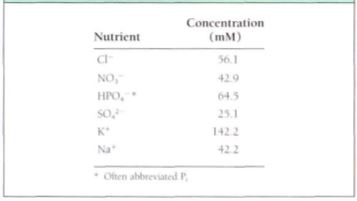
A system to excrete wastes never evolved in plants; instead, metabolic waste products are pumped across the vacuole membrane and stored permanently in the central vacuole. The tonoplast is otherwise impermeable to these wastes, so they cannot leak back into the cytoplasm where they would be harmful. Holding waste inside forever does not sound like an optimal situation, but it actually may be selectively advantageous: Because most of these compounds are noxious and bitter, they deter animals from eating the plants. Mutations that result in excretion might make the cells taste good, which would be selectively disadvantageous.
The central vacuole is a digestive organelle as well. As organelles age and become impaired, they fuse with the tonoplast and are transported into the central vacuole, where digestive enzymes break them down. The liberated monomers are presumably transported back into the rest of the cell, where they are used again. In animal cells, which do not have central vacuoles, this task is carried out by small vacuoles called lysosomes.
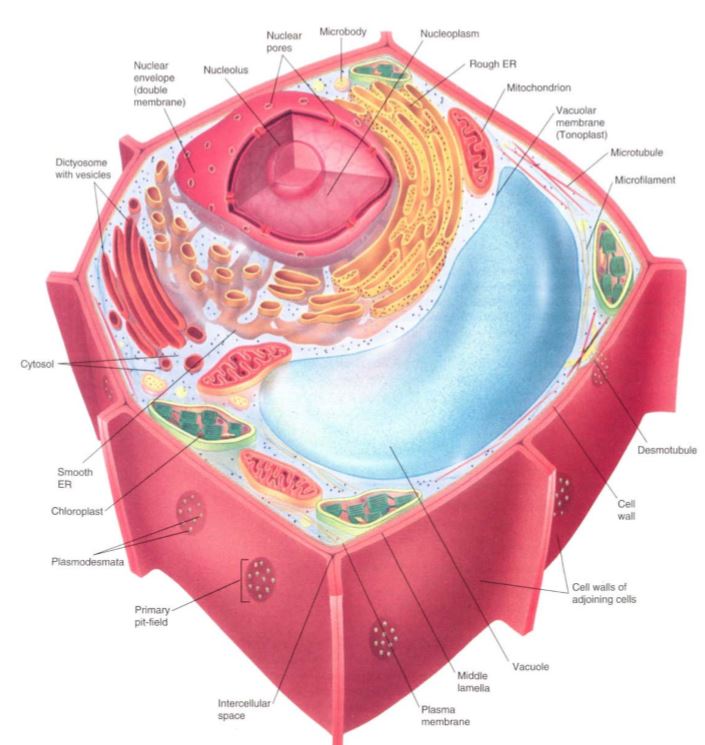
FIGURE 1: Generalized plant cell.