
Frobenius Method
 المؤلف:
Arfken, G
المؤلف:
Arfken, G
 المصدر:
Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press
المصدر:
Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press
 الجزء والصفحة:
...
الجزء والصفحة:
...
 12-6-2018
12-6-2018
 2915
2915
Frobenius Method
If  is an ordinary point of the ordinary differential equation, expand
is an ordinary point of the ordinary differential equation, expand  in a Taylor series about
in a Taylor series about  . Commonly, the expansion point can be taken as
. Commonly, the expansion point can be taken as  , resulting in the Maclaurin series
, resulting in the Maclaurin series
 |
(1)
|
Plug  back into the ODE and group the coefficients by power. Now, obtain a recurrence relation for the
back into the ODE and group the coefficients by power. Now, obtain a recurrence relation for the  th term, and write the series expansion in terms of the
th term, and write the series expansion in terms of the  s. Expansions for the first few derivatives are
s. Expansions for the first few derivatives are
If  is a regular singular point of the ordinary differential equation,
is a regular singular point of the ordinary differential equation,
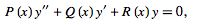 |
(7)
|
solutions may be found by the Frobenius method or by expansion in a Laurent series. In the Frobenius method, assume a solution of the form
 |
(8)
|
so that
Now, plug  back into the ODE and group the coefficients by power to obtain a recursion formula for the
back into the ODE and group the coefficients by power to obtain a recursion formula for the  th term, and then write the series expansion in terms of the
th term, and then write the series expansion in terms of the  s. Equating the
s. Equating the  term to 0 will produce the so-called indicial equation, which will give the allowed values of
term to 0 will produce the so-called indicial equation, which will give the allowed values of  in the series expansion.
in the series expansion.
As an example, consider the Bessel differential equation
 |
(13)
|
Plugging (◇) into (◇) yields
 |
(14)
|
The indicial equation, obtained by setting  , is then
, is then
![a_0[k(k-1)+k-m^2]=a_0(k^2-m^2)=0.](http://mathworld.wolfram.com/images/equations/FrobeniusMethod/NumberedEquation6.gif) |
(15)
|
Since  is defined as the first nonzero term,
is defined as the first nonzero term,  , so
, so  . For illustration purposes, ignore
. For illustration purposes, ignore  and consider only the case
and consider only the case  (avoiding the special case
(avoiding the special case  ), then equation (14) requires that
), then equation (14) requires that
 |
(16)
|
(so  ) and
) and
![[a_nn(2m+n)+a_(n-2)]x^(m+n)=0](http://mathworld.wolfram.com/images/equations/FrobeniusMethod/NumberedEquation8.gif) |
(17)
|
for  , 3, ..., so
, 3, ..., so
 |
(18)
|
for  . Plugging back in to (◇), rearranging, and simplifying then gives the series solution that defined the Bessel function of the first kind
. Plugging back in to (◇), rearranging, and simplifying then gives the series solution that defined the Bessel function of the first kind  , which is the nonsingular solution to (◇). (Considering the case
, which is the nonsingular solution to (◇). (Considering the case  proceeds analogously and results in the solution
proceeds analogously and results in the solution  .)
.)
Fuchs's theorem guarantees that at least one power series solution will be obtained when applying the Frobenius method if the expansion point is an ordinary, or regular, singular point. For a regular singular point, a Laurent seriesexpansion can also be used. Expand  in a Laurent series, letting
in a Laurent series, letting
 |
(19)
|
Plug  back into the ODE and group the coefficients by power. Now, obtain a recurrence formula for the
back into the ODE and group the coefficients by power. Now, obtain a recurrence formula for the  th term, and write the Taylor series in terms of the
th term, and write the Taylor series in terms of the  s.
s.
REFERENCES:
Arfken, G. "Series Solutions--Frobenius' Method." §8.5 in Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press, pp. 454-467, 1985.
Frobenius. "Ueber die Integration der linearen Differentialgleichungen durch Reihen." J. reine angew. Math. 76, 214-235, 1873.
Ince, E. L. Ch. 5 in Ordinary Differential Equations. New York: Dover, 1956.
 الاكثر قراءة في معادلات تفاضلية
الاكثر قراءة في معادلات تفاضلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


