

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Diels-Alder Cycloaddition
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
28-8-2018
1524
Diels-Alder Cycloaddition
The unique character of conjugated dienes manifests itself dramatically in the Diels-Alder Cycloaddition Reaction. A cycloaddition reaction is the concerted bonding together of two independent pi-electron systems to form a new ring of atoms. When this occurs, two pi-bonds are converted to two sigma-bonds, the simplest example being the hypothetical combination of two ethene molecules to give cyclobutane. This does not occur under normal conditions, but the cycloaddition of 1,3-butadiene to cyanoethene (acrylonitrile) does, and this is an example of the Diels-Alder reaction. The following diagram illustrates two cycloadditions, and introduces several terms that are useful in discussing reactions of this kind.
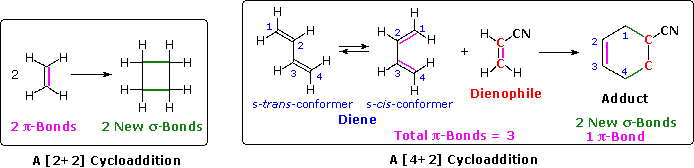
In the hypothetical ethylene dimerization on the left, each reactant molecule has a pi-bond (colored orange) occupied by two electrons. The cycloaddition converts these pi-bonds into new sigma-bonds (colored green), and this transformation is then designated a [2+2] cycloaddition, to enumerate the reactant pi-electrons that change their bonding location.
The Diels-Alder reaction is an important and widely used method for making six-membered rings, as shown on the right. The reactants used in such reactions are a conjugated diene, simply referred to as the diene, and a double or triple bond coreactant called the dienophile, because it combines with (has an affinity for) the diene. The Diels-Alder cycloaddition is classified as a [4+2] process because the diene has four pi-electrons that shift position in the reaction and the dienophile has two.
The Diels-Alder reaction is a single step process, so the diene component must adopt a cis-like conformation in order for the end carbon atoms (#1 & #4) to bond simultaneously to the dienophile. Such conformations are called s-cis, the s referring to the single bond connecting the two double bonds. The s-cis and s-trans conformers of 1,3-butadiene are shown in the preceding diagram. For many acyclic dienes the s-trans conformer is more stable than the s-cis conformer (due to steric crowding of the end groups), but the two are generally in rapid equilibrium, permitting the use of all but the most hindered dienes as reactants in Diels-Alder reactions. In its usual form, the diene component is electron rich, and the best dienophiles are electron poor due to electron withdrawing substituents such as CN, C=O & NO2. The initial bonding interaction reflects this electron imbalance, with the two new sigma-bonds being formed simultaneously, but not necessarily at equal rates.
 الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















