

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Reactions of Free Radicals : Substitution Reactions
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
28-8-2018
2937
Reactions of Free Radicals : Substitution Reactions
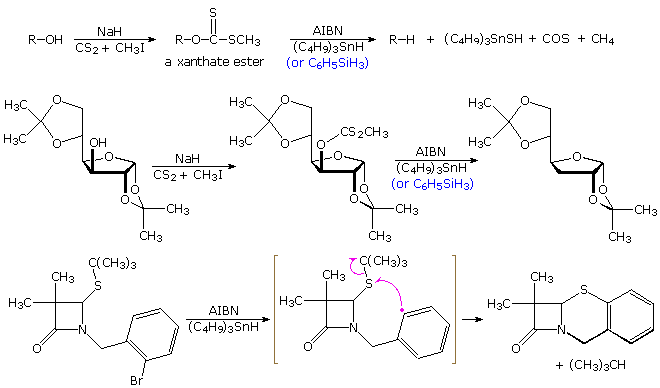
The alkyl halide reduction described above is one example of a radical substitution reaction. Two other substitution reactions are shown in the diagram below. The first two equations illustrate a useful procedure for reducing alcohols to alkanes, known as "Barton-McCombie deoxygenation". A thionoester, such as a xanthate, is first prepared from the alcohol, and then treated with tributyltin hydride and a radical initiator. Phenylsilane may be substituted for the stannane as a radical carrier. In either case a radical (X• )adds to the C=S function, and the resulting •C(OR)–S–X species fragments to R• and XSC=O. This reduction is particularly useful for 2º-alcohols, as in the second equation. Deoxygenation of 1º-alcohols is often effected by LiAlH4 reduction of tosylate derivatives, a technique that is less satisfactory for 2º-alcohols.
The second equation shows an interesting substitution of sulfur for bromine. Here the phenyl radical intermediate bonds to sulfur, followed by homolysis of the tert-butyl substituent.
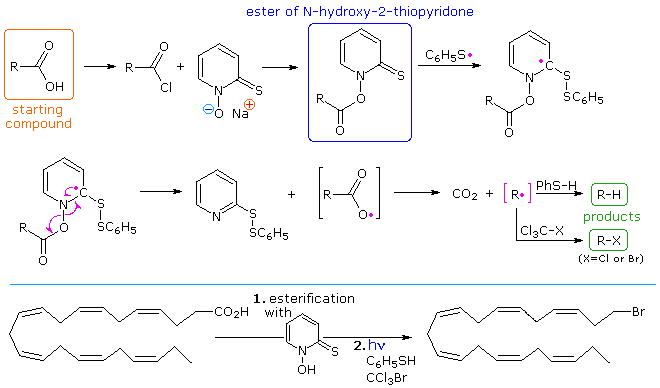
A variation of the Barton-McCombie, called "Barton decarboxylation" will be displayed above. Here advantage is taken of e weak N–O bond to generate a carboxyl radical, which rapidly decarboxylates to an alkyl radical. The N-hydroxy-2-thiopyridone derivative of a carboxylic acid or acid chloride is readily prepared. Photolysis in the presence of a thiol as the hydrogen transfer agent initiates the chain reaction shown above the light blue line. The alkyl radical thus prepared (in pink brackets) may then accept a hydrogen or halogen atom, depending on other reagents chosen for the reaction. The reaction shown below the blue line illustrates the versatility of this procedure.
 الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















