
Preparing Alkyl Halides from Alkenes: Allylic Bromination
 المؤلف:
..................
المؤلف:
..................
 المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
 الجزء والصفحة:
.................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
 25-7-2019
25-7-2019
 2545
2545
Preparing Alkyl Halides from Alkenes: Allylic Bromination
| R (in R–H) |
methyl |
ethyl |
i-propyl |
t-butyl
|
phenyl |
benzyl |
allyl |
vinyl |
Bond Dissociation Energy
(kcal/mole) |
103 |
98 |
95 |
93 |
110 |
85 |
88 |
112 |
The covalent bond homolyses that define the bond dissociation energies listed above may are described by the general equation:
R3C-H + energy ——> R3C· + H·
Since the hydrogen atom is common to all the cases cited here, we can attribute the differences in bond dissociation energies to differences in the stability of the alkyl radicals (R3C·) as the carbon substitution changes. This leads us to the conclusion that:
| alkyl radical stability increases in the order: phenyl < primary (1º) < secondary (2º) < tertiary (3º) < allyl ≈ benzyl. |
Because alkyl radicals are important intermediates in many reactions, this stability relationship will prove to be very useful in future discussions. The enhanced stability of allyl and benzyl radicals may be attributed to resonance stabilization.
Formulas for the allyl and benzyl radicals are shown below. Draw structural formulas for the chief canonical forms contributing to the resonance hybrid in each case.
The poor stability of phenyl radicals, C6H5·, may in turn be attributed to the different hybridization state of the carbon bearing the unpaired electron (sp2 vs. sp3).
We noted that benzylic and allylic sites are exceptionally reactive in free radical halogenation reactions. Since carbon-carbon double bonds add chlorine and bromine in liquid phase solutions, radical substitution reactions by these halogens are often carried out at elevated temperature in the gas phase (first equation below). Formation of the ionic π-complexes that are intermediates in halogen addition is unfavorable in the absence of polar solvents, and entropy generally favors substitution over addition.
The brominating reagent, N-bromosuccinimide (NBS), has proven useful for achieving allylic or benzylic substitution in CCl4 solution at temperatures below its boiling point (77 ºC). One such application is shown in the second equation.
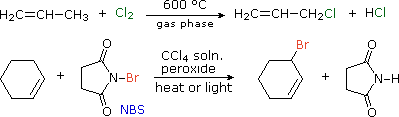
The predominance of allylic substitution over addition in the NBS reaction is interesting. The N–Br bond is undoubtedly weak (probably less than 50 kcal/mol) so bromine atom abstraction by radicals should be very favorable. The resulting succinimyl radical might then establish a chain reaction by removing an allylic hydrogen from the alkene. One problem with this mechanism is that NBS is very insoluble in CCl4, about 0.006 mole / liter at reflux. Although it is possible that the allylic bromination occurs at a solid-liquid interface, evidence for another pathway has been obtained. In the non-polar solvent used for these reactions, very low concentrations of bromine may be generated from NBS. This would serve as a source of bromine atoms, which would abstract allylic hydrogens irreversibly (an exothermic reaction) in competition with reversible addition to the double bond. The HBr produced in this way is known to react with NBS, giving a new bromine molecule and succinimide, as shown here. Ionic addition of bromine to the double bond would be very slow in these circumstances (CCl4 is a nonpolar solvent).
HBr + (CH2CO)2NBr → Br2 + (CH2CO)2NH
This mechanism is essentially the same as that for the free radical halogenation of alkanes, with NBS serving as a source of very low concentrations of bromine. Unsymmetrical allylic radicals will react to give two regioisomers. Thus, 1-octene on bromination with NBS yields a mixture of 3-bromo-1-octene (ca. 18%) and 1-bromo-2-octene (82%) - both cis and trans isomers.
RCH2CH=CH2 + (CH2CO)2NBr → RCHBrCH=CH2 + RCH=CHCH2Br + (CH2CO)2N
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


