

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Reactivity in E1 reactions
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
3-8-2019
1423
Reactivity in E1 reactions
Due to the fact that E1 reactions create a carbocation intermediate, rules present in SN1
reactions still apply.
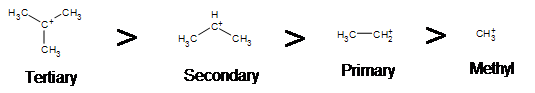
As expected, tertiary carbocations are favored over secondary, primary and methyl’s. This is due to the phenomena of hyperconjugation, which essentially allows a nearby C-C or C-H bond to interact with the p orbital of the carbon to bring the electrons down to a lower energy state. Thus, this has a stabilizing effect on the molecule as a whole. In general, primary and methyl carbocations do not proceed through the E1 pathway for this reason, unless there is a means of carbocation rearrangement to move the positive charge to a nearby carbon. Secondary and Tertiary carbons form more stable carbocations, thus this formation occurs quite rapidly.
Secondary carbocations can be subject to the E2 reaction pathway, but this generally occurs in the presence of a good / strong base. Adding a weak base to the reaction disfavors E2, essentially pushing towards the E1 pathway. In many instances, solvolysis occurs rather than using a base to deprotonate. This means heat is added to the solution, and the solvent itself deprotonates a hydrogen. The medium can effect the pathway of the reaction as well. Polar protic solvents may be used to hinder nucleophiles, thus disfavoring E2 / Sn2 from occurring.
 الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















