

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Mass Spectrometry of Some Common Functional Groups
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
5-8-2019
1558
Mass Spectrometry of Some Common Functional Groups
Much of the utility in electron-ionization MS comes from the fact that the radical cations generated in the electron-bombardment process tend to fragment in predictable ways. Detailed analysis of the typical fragmentation patterns of different functional groups is beyond the scope of this text, but it is worthwhile to see a few representative examples, even if we don’t attempt to understand the exact process by which the fragmentation occurs. We saw, for example, that the base peak in the mass spectrum of acetone is m/z = 43. This is the result of cleavage at the ‘alpha’ position - in other words, at the carbon-carbon bond adjacent to the carbonyl. Alpha cleavage results in the formation of an acylium ion (which accounts for the base peak at m/z = 43) and a methyl radical, which is neutral and therefore not detected.
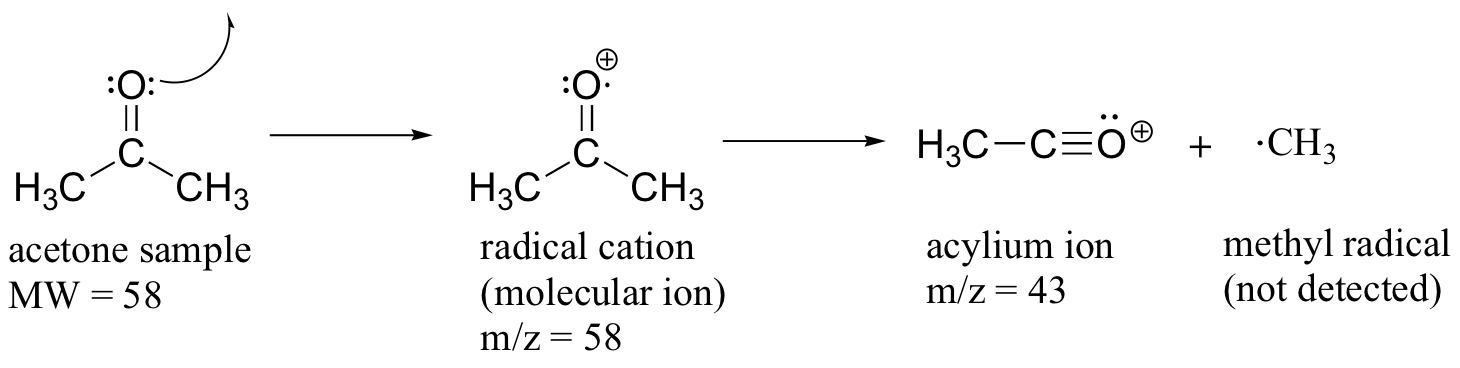
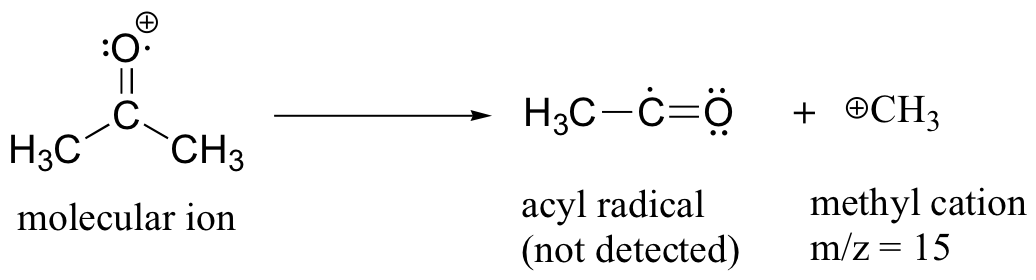
After the parent peak and the base peak, the next largest peak, at a relative abundance of 23%, is at m/z = 15. This, as you might expect, is the result of formation of a methyl cation, in addition to an acyl radical (which is neutral and not detected).
A common fragmentation pattern for larger carbonyl compounds is called the McLafferty rearrangement:
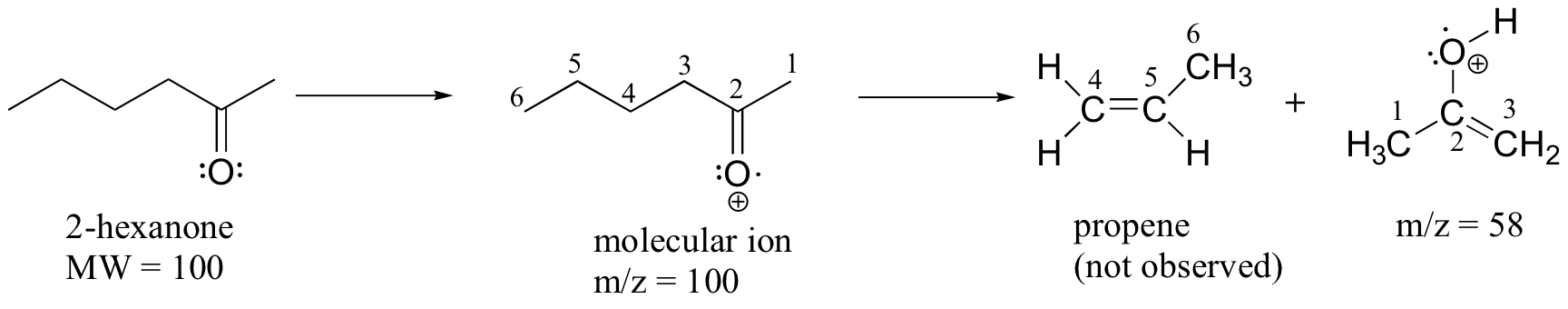
The mass spectrum of 2-hexanone shows a 'McLafferty fragment' at m/z = 58, while the propene fragment is not observed because it is a neutral species (remember, only cationic fragments are observed in MS). The base peak in this spectrum is again an acylium ion.

When alcohols are subjected to electron ionization MS, the molecular ion is highly unstable and thus a parent peak is often not detected. Often the base peak is from an ‘oxonium’ ion.

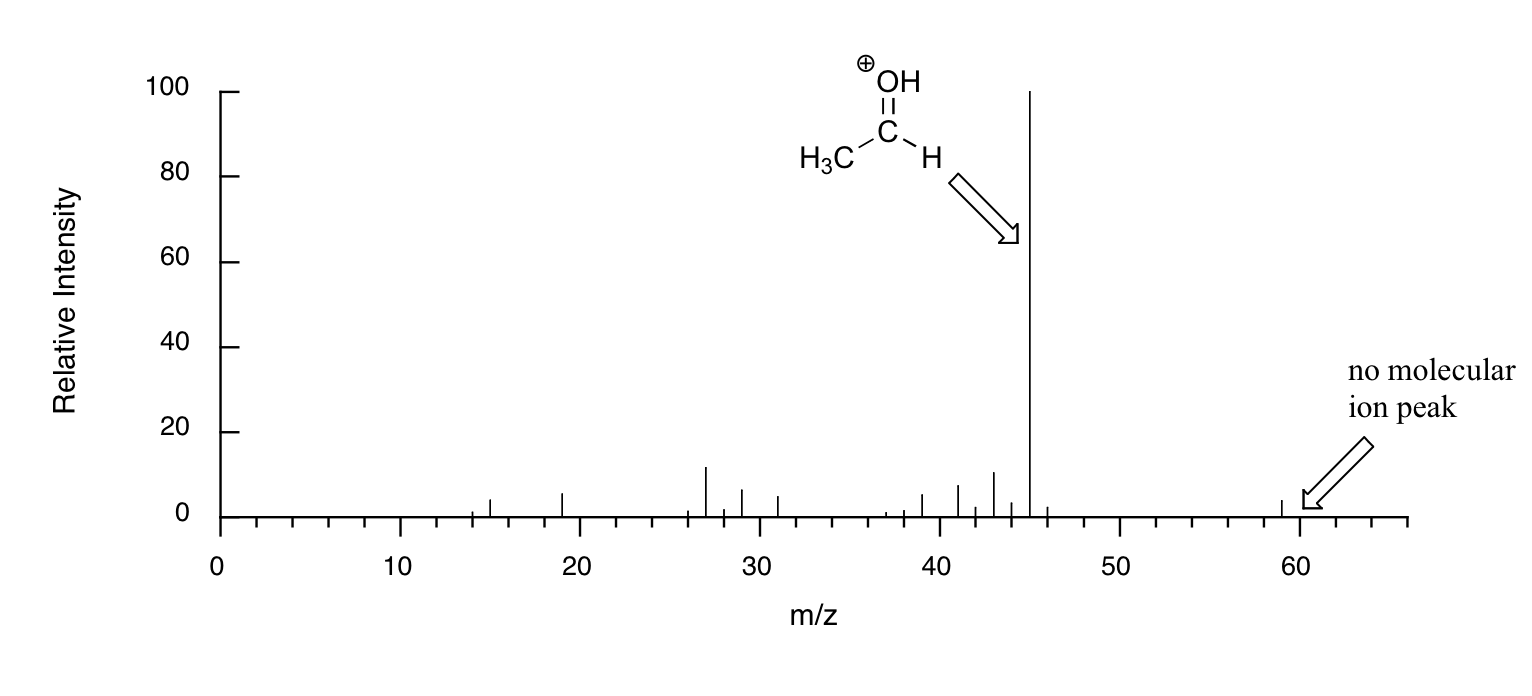
Other functional groups have predictable fragmentation patterns as well. By carefully analyzing the fragmentation information that a mass spectrum provides, a knowledgeable spectrometrist can often ‘put the puzzle together’ and make some very confident predictions about the structure of the starting sample.
 الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















