The basics of an NMR experiment
Given that chemically nonequivalent protons have different resonance frequencies in the same applied magnetic field, we can see how NMR spectroscopy can provide us with useful information about the structure of an organic molecule. A full explanation of how a modern NMR instrument functions is beyond the scope of this text, but in very simple terms, here is what happens. First, a sample compound (we'll use methyl acetate) is placed inside a very strong applied magnetic field (B0).
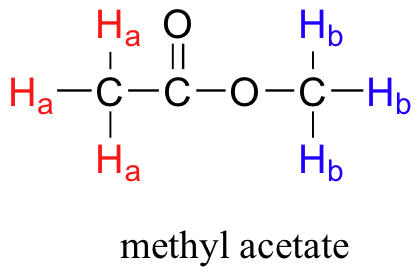
All of the protons begin to precess: the Ha protons at precessional frequency ωa, the Hb protons at ωb.At first, the magnetic moments of (slightly more than) half of the protons are aligned with B0, and half are aligned against B0. Then, the sample is hit with electromagnetic radiation in the radio frequency range. The two specific frequencies which match ωaandωb(i.e. the resonance frequencies) cause those Ha and Hb protons which are aligned with B0 to 'flip' so that they are now aligned against B0. In doing so, the protons absorb radiation at the two resonance frequencies. The NMR instrument records which frequencies were absorbed, as well as the intensity of each absorbance.
In most cases, a sample being analyzed by NMR is in solution. If we use a common laboratory solvent (diethyl ether, acetone, dichloromethane, ethanol, water, etc.) to dissolve our NMR sample, however, we run into a problem – there many more solvent protons in solution than there are sample protons, so the signals from the sample protons will be overwhelmed. To get around this problem, we use special NMR solvents in which all protons have been replaced by deuterium. Recall that deuterium is NMR-active, but its resonance frequency is very different from that of protons, and thus it is `invisible` in 1H-NMR. Some common NMR solvents are shown below.