


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 17-12-2019
Date: 11-7-2019
Date: 17-12-2019
|
Many enzymes are simple proteins consisting entirely of one or more amino acid chains. Other enzymes contain a nonprotein component called a cofactor that is necessary for the enzyme’s proper functioning. There are two types of cofactors: inorganic ions [e.g., zinc or Cu(I) ions] and organic molecules known as coenzymes. Most coenzymes are vitamins or are derived from vitamins.
Vitamins are organic compounds that are essential in very small (trace) amounts for the maintenance of normal metabolism. They generally cannot be synthesized at adequate levels by the body and must be obtained from the diet. The absence or shortage of a vitamin may result in a vitamin-deficiency disease. In the first half of the 20th century, a major focus of biochemistry was the identification, isolation, and characterization of vitamins. Despite accumulating evidence that people needed more than just carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in their diets for normal growth and health, it was not until the early 1900s that research established the need for trace nutrients in the diet.
Because organisms differ in their synthetic abilities, a substance that is a vitamin for one species may not be so for another. Over the past 100 years, scientists have identified and isolated 13 vitamins required in the human diet and have divided them into two broad categories: the fat-soluble vitamins (Table 2), which include vitamins A, D, E, and K, and the water-soluble vitamins, which are the B complex vitamins and vitamin C (Table 3). All fat-soluble vitamins contain a high proportion of hydrocarbon structural components. There are one or two oxygen atoms present, but the compounds as a whole are nonpolar. In contrast, water-soluble vitamins contain large numbers of electronegative oxygen and nitrogen atoms, which can engage in hydrogen bonding with water. Most water-soluble vitamins act as coenzymes or are required for the synthesis of coenzymes. The fat-soluble vitamins are important for a variety of physiological functions.
One characteristic that distinguishes an enzyme from all other types of catalysts is its substrate specificity. An inorganic acid such as sulfuric acid can be used to increase the reaction rates of many different reactions, such as the hydrolysis of disaccharides, polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins, with complete impartiality. In contrast, enzymes are much more specific. Some enzymes act on a single substrate, while other enzymes act on any of a group of related molecules containing a similar functional group or chemical bond. Some enzymes even distinguish between D- and L-stereoisomers, binding one stereoisomer but not the other. Urease, for example, is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a single substrate—urea—but not the closely related compounds methyl urea, thiourea, or biuret. The enzyme carboxypeptidase, on the other hand, is far less specific. It catalyzes the removal of nearly any amino acid from the carboxyl end of any peptide or protein.
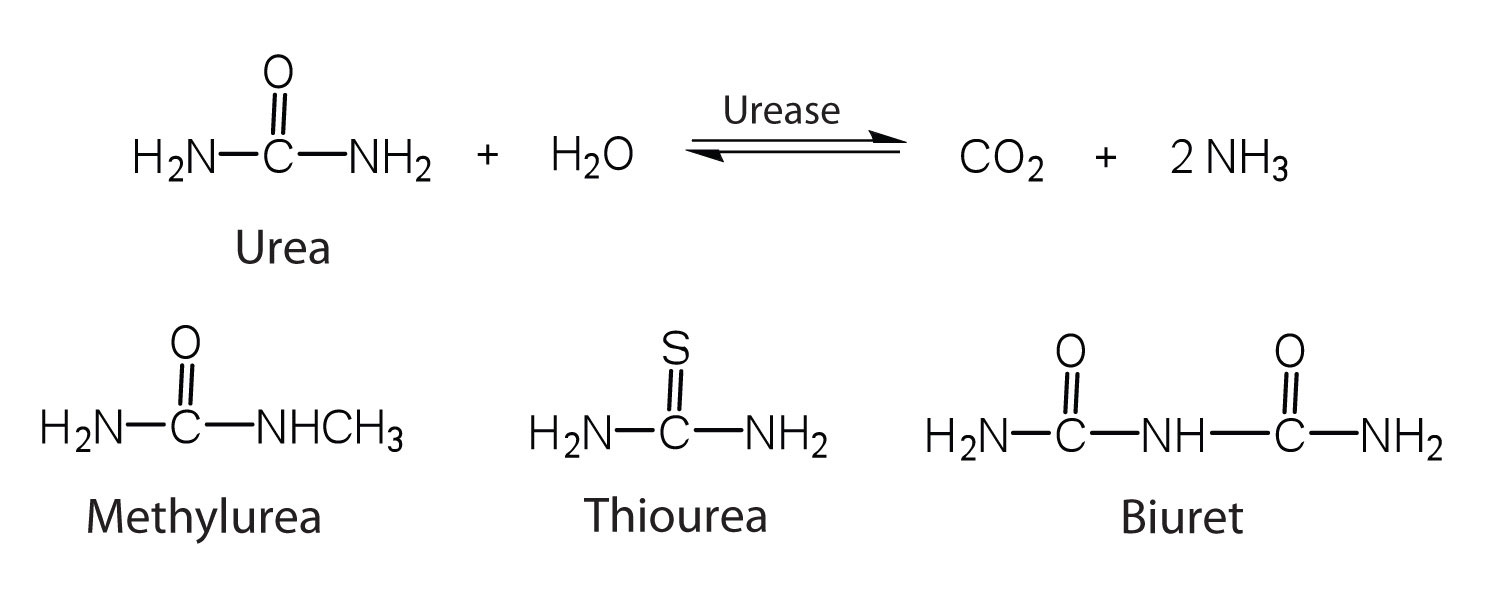
Enzyme specificity results from the uniqueness of the active site in each different enzyme because of the identity, charge, and spatial orientation of the functional groups located there. It regulates cell chemistry so that the proper reactions occur in the proper place at the proper time. Clearly, it is crucial to the proper functioning of the living cell.



|
|
|
|
دراسة: حفنة من الجوز يوميا تحميك من سرطان القولون
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تنشيط أول مفاعل ملح منصهر يستعمل الثوريوم في العالم.. سباق "الأرنب والسلحفاة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
لتعزيز التواصل مع الزائرات الأجنبيات : العتبة العلويّة المقدّسة تُطلق دورة لتعليم اللغة الإنجليزية لخادمات القسم النسويّ
|
|
|