
Quantum efficiency
 المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
 المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 283
الجزء والصفحة:
p 283
 23-8-2020
23-8-2020
 1836
1836
Quantum efficiency
Besides knowing the spectral response of any detector in a relative way, it is important to know how efficient it is in producing a response in relation to the quantity of radiation which falls on to it. This can be conveniently expressed in terms of its quantum efficiency.
In many cases where light interacts with matter, such as in a detector, the interaction can only be described by assigning a ‘particle’ nature to the radiation. This description requires that a beam of radiation be made up of discrete packets of energy called photons or quanta. As presented in earlier chapters, the energy, E, carried by each quantum is given by
E = hν
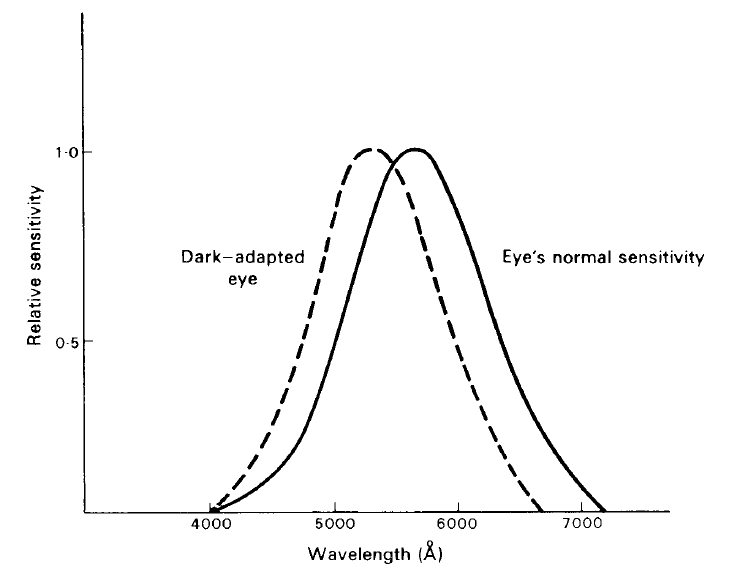
Figure 1. The relative spectral sensitivity of an average human eye; the dotted curve illustrates the Purkinje effect, showing how the sensitivity curve is modified when the eye is dark-adapted.
where h is Planck’s constant, equal to 6·63 × 10−34 J s and ν is the frequency of the electromagnetic wave. It is easy, therefore, to perform the conversion between the amount of energy in a beam, given in watts for example, to the number of photons s−1 which are travelling with the beam—as done, for example.
From the size of response of a detector to a beam of light whose energy is known in terms of photons s−1, it is possible to evaluate the fraction of the photons which are effectively used to provide the response. The ratio of the number of photons present in the beam to the number which contribute to the detector’s response defines the quantum efficiency of the detector.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


