
Image converters
 المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
 المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 299
الجزء والصفحة:
p 299
 25-8-2020
25-8-2020
 1902
1902
Image converters
An image converter or image intensifier, now disappearing from regular use, is a device which uses a combination of photoelectric and photographic processes (see figure 1). Primary detection of an image is achieved by using a photocathode, giving the benefits of its relatively high quantum efficiency. By a system of accelerating electrodes, the photoelectrons gain energy and are made to impinge on a phosphor which then liberates light according to the number of electrons it receives. Immediately behind the phosphor is placed a photographic plate which records the intensity distribution across the phosphor. The light to which the final exposure is made is much stronger than the original amount falling on the photocathode, the amplification depending on the energy which the accelerated electrons have gained in transit through the tube and on the efficiency of the phosphor.
The accelerating electrodes also provide a means of focusing the trajectories of each electron which is emitted by the photocathode. By this means, any point in the phosphor where an electron arrives corresponds to a particular single point on the surface of the photocathode. This, in turn, corresponds to a single point in the primary image. On the plates behind the phosphor, there is a one-to-one correspondence between the recorded image and the detail in the original image. The image converter is, thus, capable of obtaining images of extended objects efficiently by using the good quantum efficiency of photocathode material and the spatial recording ability of a photographic plate.
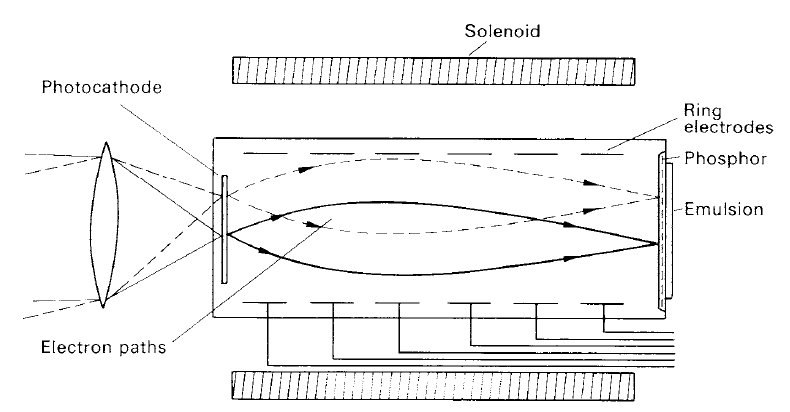
Figure 1. A simple image intensifier. Electrons ejected from the photocathode are focused on the emulsion-backed phosphor by uniform electric and magnetic fields.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


