We end this chapter with a discussion of a type of reaction that is different from anything we have seen before. In the Diels-Alder cycloaddition reaction, a conjugated diene reacts with an alkene to form a ring structure.

In a Diels-Alder reaction, the alkene reacting partner is referred to as the dienophile. Essentially, this process involves overlap of the 2p orbitals on carbons 1 and 4 of the diene with 2p orbitals on the two sp2-hybridized carbons of the dienophile. Both of these new overlaps end up forming new sigma bonds, and a new pi bond is formed between carbon 2 and 3 of the diene.One of the most important things to understand about this process is that it is concerted – all of the electron rearrangement takes place at once, with no carbocation intermediates.The Diels-Alder reaction is enormously useful for synthetic organic chemists, not only because ring-forming reactions are useful in general but also because in many cases two new stereocenters are formed, and the reaction is inherently stereospecific. A cis dienophile will generate a ring with cis substitution, while a trans dienophile will generate a ring with trans substitution:

In order for a Diels-Alder reaction to occur, the diene molecule must adopt what is called the

s-cis conformation:The s-cis conformation is higher in energy than the s-trans conformation, due to steric hindrance. For some dienes, extreme steric hindrance causes the s-cis conformation to be highly strained, and for this reason such dienes do not readily undergo Diels-Alder reactions.

Cyclic dienes, on the other hand, are ‘locked’ in the s-cis conformation, and are especially reactive. The result of a Diels-Alder reaction involving a cyclic diene is a bicyclic structure:

Here, we see another element of stereopecificity: Diels-Alder reactions with cyclic dienes favor the formation of bicyclic structures in which substituents are in the endo position.

The endo position on a bicyclic structure refers to the position that is inside the concave shape of the larger (six-membered) ring. As you might predict, the exo position refers to the outside position.
The rate at which a Diels-Alder reaction takes place depends on electronic as well as steric factors. A particularly rapid Diels-Alder reaction takes place between cyclopentadiene and maleic anhydride.

We already know that cyclopentadiene is a good diene because of its inherent s-cis conformation. Maleic anhydride is also a very good dienophile, because the electron-withdrawing effect of the carbonyl groups causes the two alkene carbons to be electron-poor, and thus a good target for attack by the pi electrons in the diene.
In general, Diels-Alder reactions proceed fastest with electron-donating groups on the diene (eg. alkyl groups) and electron-withdrawing groups on the dienophile.
Alkynes can also serve as dienophiles in Diels-Alder reactions:

Below are just three examples of Diels-Alder reactions that have been reported in recent years:



The Diels-Alder reaction is just one example of a pericyclic reaction: this is a general term that refers to concerted rearrangements that proceed though cyclic transition states. Two well-studied intramolecular pericyclic reactions are known as the Cope rearrangement . . .

. . .and the Claisen rearrangement (when an oxygen is involved):

Notice that the both of these reactions require compounds in which two double bonds are separated by three single bonds.
Pericyclic reactions are rare in biological chemistry, but here is one example: the Claisen rearrangement catalyzed by chorismate mutase in the aromatic amino acid biosynthetic pathway.
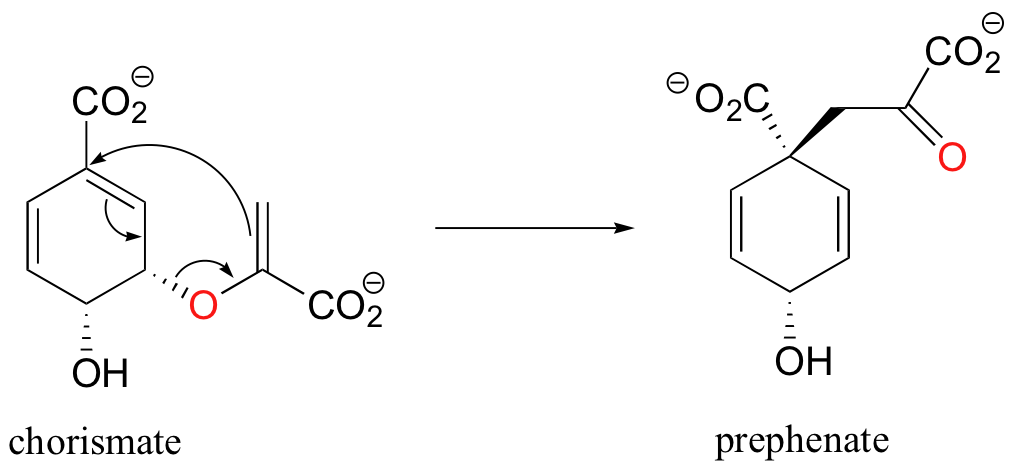
The study of pericyclic reactions is an area of physical organic chemistry that blossomed in the mid-1960s, due mainly to the work of R.B. Woodward, Roald Hoffman, and Kenichi Fukui. The Woodward-Hoffman rules for pericyclic reactions (and a simplified version introduced by Fukui) use molecular orbital theory to explain why some pericyclic processes take place and others do not. A full discussion is beyond the scope of this text, but if you go on to study organic chemistry at the advanced undergraduate or graduate level you are sure to be introduced to this fascinating area of inquiry.
















 الاكثر قراءة في
الاكثر قراءة في  اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار



 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















