
POINT OF VIEW
 المؤلف:
S. Gibilisco
المؤلف:
S. Gibilisco
 المصدر:
Physics Demystified
المصدر:
Physics Demystified
 الجزء والصفحة:
532
الجزء والصفحة:
532
 11-11-2020
11-11-2020
 2945
2945
POINT OF VIEW
Suppose that there are eight clocks in space arranged at the vertices of a gigantic cube. Each edge of the cube measures 1 light-minute, or approximately 1.8 × 107 km (1.1 × 107 mi), long, as shown in Fig. 20-1. We are given a challenge: Synchronize the clocks so that they agree within the limit of visibility, say, to within 1 second of each other. Do you suppose that this will be easy?
Because the clocks are so far apart, the only way we can ascertain what they say is to equip them with radio transmitters that send time signals. Alternatively, if we have a powerful enough telescope, we can observe them and read them directly by sight. In either case, the information that tells us what the clocks say travels to us at the speed of light. We get in our space ship and maneuver ourselves so that we are in the exact center of the cube, equidistant from all eight clocks. Then we proceed to synchronize them using remote-control, wireless two-way data communications equipment.
Thank heaven for computers! The task is accomplished in a just a few minutes. It can’t be done instantaneously, of course, because our command signals take the better part of a minute to reach the clocks from our central location, and then the signals coming back from the clocks take just as long to get to us so that we can see what they say. Soon, however,
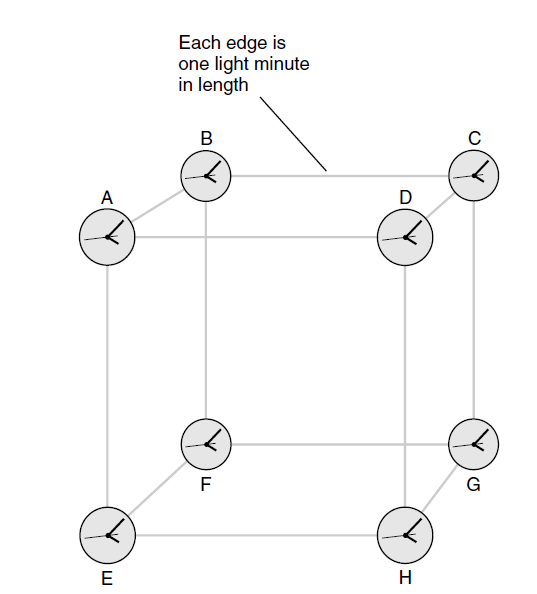
Fig. 1. A hypothetical set of eight clocks arranged at the vertices of a cube that measures 1 light-minute on each edge. How will we synchronize these clocks?
everything is in agreement. Clocks A through H all tell the same time to within a fraction of a second.
Satisfied with our work, we cruise out of the cube. We take a look back at the clocks. What do we see? The clocks have already managed to get out of sync. We take our ship back to the center of the cube to correct the problem. When we get there, however, there is no problem to correct! The clocks are all in agreement again.
You can guess what is happening here. The clock readings depend on how far their signals must travel to reach us. For an observer at the center of the cube, the signals from all eight clocks, A through H, arrive from exactly the same distance. However, this is not true for any other point in space. Therefore, the clocks can be synchronized only for that one favored point; if we go somewhere else, we will have to synchronize them all over again. This can be done, but then the clocks will be synchronized only when observed from the new favored vantage point. There is a unique sync point—the spot in space from which all eight clocks read the same—for each coordination of the clocks.
No sync point is more valid than any other from a scientific standpoint. If the cube happens to be stationary relative to some favored reference point such as the Earth, we can synchronize the clocks, for convenience, from that reference point. However, if the cube is moving relative to our frame of reference, we will never be able to keep the clocks synchronized. Time depends on where we are and on whether or not we are moving relative to whatever device we use to indicate the time. Time is not absolute, but relative, and there is no getting around it.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


