


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 22-5-2021
Date: 16-5-2021
Date: 16-5-2021
|
Possessive Adjectives – Definition and Examples:
Also called possessive determiners, possessive adjectives refer to words which modify a noun by showing a form of possession or a sense of belonging to a particular person or thing. This article will provide useful information on the different forms of possessive adjectives, the different functions, some tips on their usage, as well as some examples that can serve as your reference.
What are the Definition and Functions of Possessive Adjectives?
As mentioned earlier, possessive adjectives are the words used to show a form of possession/ ownership or are used to express a close relationship with someone or something. Moreover, just like the article “the,” a possessive adjective also implies definiteness. Some of the most basic possessive adjectives that are commonly used in the English language are: my, your, our, its, her, his, their, and whose (interrogative).
Examples:
Whose bag is this?
In this interrogative sentence, the italicized word “whose” is used to express ownership for the noun “bag.”
That is his baseball cap.
In the sentence above, the possessive adjective “his” shows who owns the noun “baseball cap.”
I think Lea will miss her.
Although the possessive adjective “her” is used in the sample sentence above, it does not necessarily mean that Lea owns the “flight.” The phrase “her flight” just refers to the flight that Lea will take and travel on.
My mother is here.
Obviously, one cannot own a specific person. So in this example, the possessive adjective “my” indicates a close personal relationship with the noun “mother.”
I really like your.
In the sentence above, the possessive adjective “your” shows who owns the noun “jacket.”
Other Examples:
His name is Kevin.
Her name is Michaela.
Our cat is always licking its body.
We sold our dune buggy yesterday.
The children thanked their teacher.
What is the Difference Between Possessive Adjectives and Possessive Pronouns?
Although the possessive adjectives and possessive pronouns are closely related and can sometimes be confusing, it is actually very easy to differentiate one from the other. Basically, you just have to remember that possessive pronouns are used in place of a noun. Take a look at the example below:
Gian’s jacket is black. Hers is brown.
In the sentence above, instead of mentioning another name (noun), the possessive pronoun “hers” is used as a replacement.
On the other hand, possessive adjectives are used to modify a noun and just like ordinary adjectives, they are located before the word that it describes. For example:
My dirt bike is faster than his moped.
What are the Different Forms of Possessive Adjectives?
Below are the different forms of possessive adjectives:
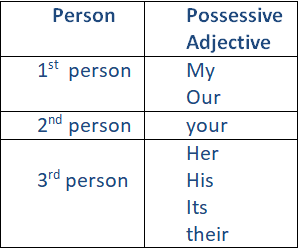
Example:
We sold our dune buggy yesterday.The 1st person possessive adjectives “my” and “our” can be used for both male and female owners. However, the possessive adjective “my” is for singular owners, while the possessive adjective “our” is for plural ones.
This means that the dune buggy does not solely belong to the speaker. It can be a family vehicle, for instance.
The 2nd person possessive adjective “your” can be used for both male and female owners, and also for both singular and plural owners.
Examples:
Jack doesn’t have your phone number, Karen.In this sentence, the possessive adjective “your” is used for the singular owner of the phone number which is “Karen.”
Kids, don’t forget to drink your
The possessive adjective “your” is used to show ownership for the noun “milk.” Take note that in this sentence, the milk belongs to the plural noun “kids.”
The 3rd person possessive adjectives “her,” “his,” and “its” are all used if the owner is singular, while the 3rd person possessive adjective “their” is used only if the owner is in its plural form. Moreover, the possessive adjective “her” is obviously used if the owner is a female and the possessive adjective “his” is for male owners.
Examples:
His name is Kevin. (Kevin is a name for a male person)
Her name is Michaela. (Michaela is obviously a name for a female person.)
The children thanked their (The word “children” is the plural form of “child.” Therefore the 3rd person possessive adjective “their” is appropriate to use.)
Additional Tips:
The words “its” and “it’s” are almost the same except for the presence of an apostrophe in the second word. Although the apostrophe may seem trivial, it actually makes a big difference. Always remember that “it’s” is the contracted form of “it is” or “it has,” so basically if you want to use a possessive adjective in your sentence, you must use the one without an apostrophe.
Final Thoughts:
Although possessive adjectives can be confusing at first, especially because they are closely related to possessive pronouns, do not get too intimidated by these. Just by studying the contents of this article and practicing constantly on the application of this kind of words, you will surely be able to fully understand the concept. Anyway, you probably already have been using possessive adjectives for a long time and you’re just not aware of it.
|
|
|
|
دراسة تحدد أفضل 4 وجبات صحية.. وأخطرها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام الجواد (عليه السلام) في مشاتل الكفيل
|
|
|