
Vasculature and Innervation
 المؤلف:
Kelly M. Harrell and Ronald Dudek
المؤلف:
Kelly M. Harrell and Ronald Dudek
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Anatomy
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Anatomy
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 10-7-2021
10-7-2021
 3024
3024
Vasculature and Innervation
A. Vasculature
Vascular supply to the spinal cord and vertebral column originates from a number of sources (Fig. 1).
1. Arterial supply: Arterial supply to the spinal cord and vertebral column includes branches of segmental spinal arteries along the length of the cord/column.
a. Medullary arteries: The singular anterior spinal artery and paired posterior spinal arteries originate from the vertebral arteries and run the length of the spinal cord. Spinal arteries receive collateral circulation from a series of segmental medullary arteries that originate from vertebral, deep cervical, ascending cervical, posterior intercostal, lumbar, and lateral sacral arteries. The largest of these is the great anterior segmental medullary artery (artery of Adamkiewicz), which serves the lower two thirds of the spinal cord.
b. Radicular arteries: Radicular arteries supply the meningeal coverings and spinal nerve roots, but do not anastomose with spinal arteries.
c. Periosteal and equatorial branches supply arterial blood to the vertebral column (Fig. 2). Spinal branches also contribute to the bone surrounding the spinal canal. These branches arise from cervical (vertebral and ascending cervical arteries) and segmental arteries in the thoracic and lumbar regions (posterior intercostal, subcostal, lumbar, iliolumbar, and sacral arteries).
2. Venous drainage: Venous drainage of the vertebral column arises from spinal veins that originate from surrounding internal and external venous plexuses. These veins drain into segmental thoracic and lumbar veins as well as vertebral veins in the cervical
region. Venous drainage occurs through three anterior and three posterior spinal veins and a series of anterior and posterior medullary and radicular veins. These veins communicate with the internal vertebral venous plexus, which is continuous with the dural venous sinuses in the cranial vault.
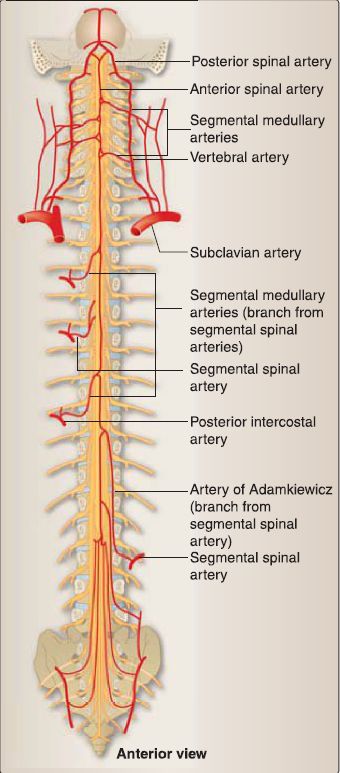
Figure 1: Primary arterial blood supply of the spinal caret
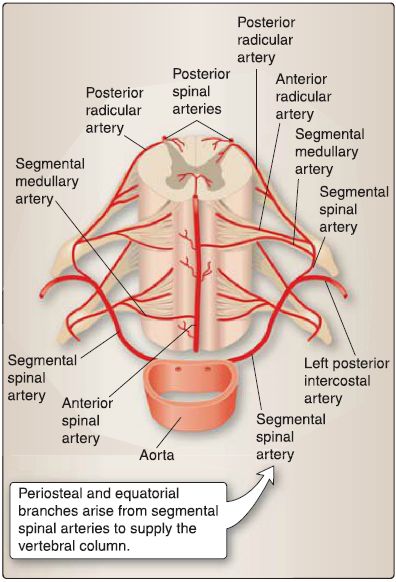
Figure 2: Cross section through spinal cord showing internal and external arterial
supply.
B. Innervation
In general, the vertebral column receives innervation from spinal nerves, specifically meningeal branches (Fig.3). These branches supply intervertebral discs, periosteum, ligaments, dura mater, and spinal blood vessels. In addition, each zygapophyseal (facet) joint is innervated by articular medial branches of posterior rami from adjacent spinal nerves, giving the synovial joint a dual innervation.
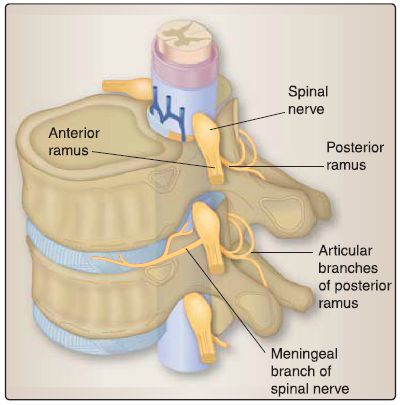
Figure 3: Neurovascular supply to the vertebral column.
 الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


