
Competitive inhibition
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 7-9-2021
7-9-2021
 2087
2087
Competitive inhibition
This type of inhibition occurs when the inhibitor binds reversibly to the same site that the substrate would normally occupy and, therefore, competes with the substrate for that site.
1. Effect on Vmax: The effect of a competitive inhibitor is reversed by increasing the concentration of substrate. At a sufficiently high [S], the reaction velocity reaches the Vmax observed in the absence of inhibitor, that is, Vmax is unchanged (Fig. 1).
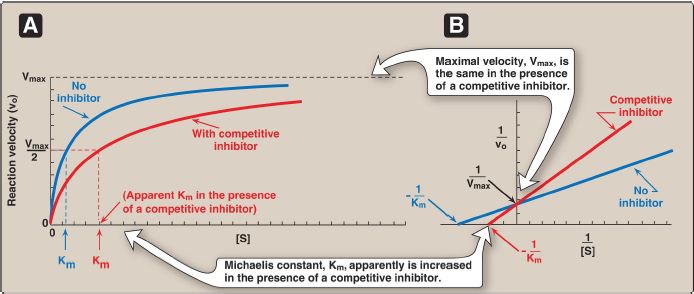
Figure 1: A. Effect of a competitive inhibitor on the reaction velocity versus substrate concentration ([S]) plot. B. Lineweaver-Burk plot of competitive inhibition of an enzyme. [Note: The slope increases if inhibitor concentration increases.]
2. Effect on Km: A competitive inhibitor increases the apparent Km for a given substrate. This means that, in the presence of a competitive inhibitor, more substrate is needed to achieve one half Vmax.
3. Effect on the Lineweaver-Burk plot: Competitive inhibition shows a characteristic Lineweaver-Burk plot in which the plots of the inhibited and uninhibited reactions intersect on the y axis at 1/Vmax (Vmax is unchanged). The inhibited and uninhibited reactions show different xaxis intercepts, indicating that the apparent Km is increased in the presence of the competitive inhibitor because − 1/Km moves closer to zero from a negative value (see Fig. 1). [Note: An important group of competitive inhibitors are the transition state analogs, stable molecules that approximate the structure of the transition state, and, therefore, bind the enzyme more tightly than does the substrate.]
4. Statin drugs as examples of competitive inhibitors: This group of antihyperlipidemic agents competitively inhibits the rate-limiting (slowest) step in cholesterol biosynthesis. This reaction is catalyzed by hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMG CoA reductase). Statins, such as atorvastatin (Lipitor) and pravastatin (Pravachol), are structural analogs of the natural substrate for this enzyme and compete effectively to inhibit HMG CoA reductase. By doing so, they inhibit de novo cholesterol synthesis, thereby lowering plasma cholesterol levels (Fig. 2).
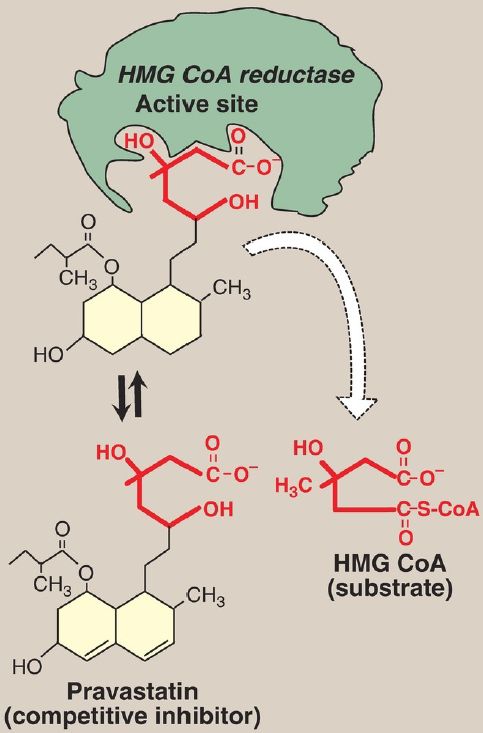
Figure 2: Pravastatin competes with hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA) for the active site of HMG CoA reductase.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


