
Steps in Translation :Termination
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 28-12-2021
28-12-2021
 1867
1867
Steps in Translation :Termination
Termination occurs when one of the three termination codons moves into the A site. These codons are recognized in E. coli by release factors: RF-1, which recognizes UAA and UAG, and RF-2, which recognizes UGA and UAA. The binding of these release factors results in hydrolysis of the bond linking the peptide to the tRNA at the P site, causing the nascent protein to be released from the ribosome. A third release factor, RF-3-GTP, then causes the release of RF-1 or RF-2 as GTP is hydrolyzed (see Fig. 1).
[Note: Eukaryotes have a single release factor, eRF, which recognizes all three termination codons. A second factor, eRF-3, functions like the prokaryotic RF-3. See Figure 2 for a summary of the factors used in translation.] The steps in prokaryotic protein synthesis, as well as some antibiotic inhibitors of the process, are summarized in Figure 1. The newly synthesized polypeptide may undergo further modification as
described below, and the ribosomal subunits, mRNA, tRNA, and protein factors can be recycled and used to synthesize another polypeptide. [Note: In prokaryotes, ribosome recycling factors mediate separation of the subunits. In eukaryotes, eRF and ATP hydrolysis are required.]
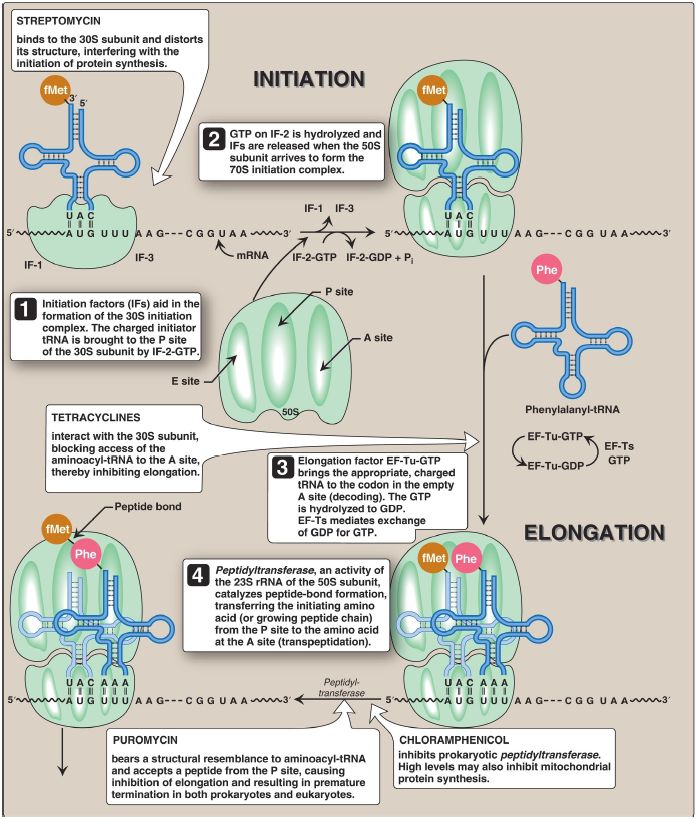
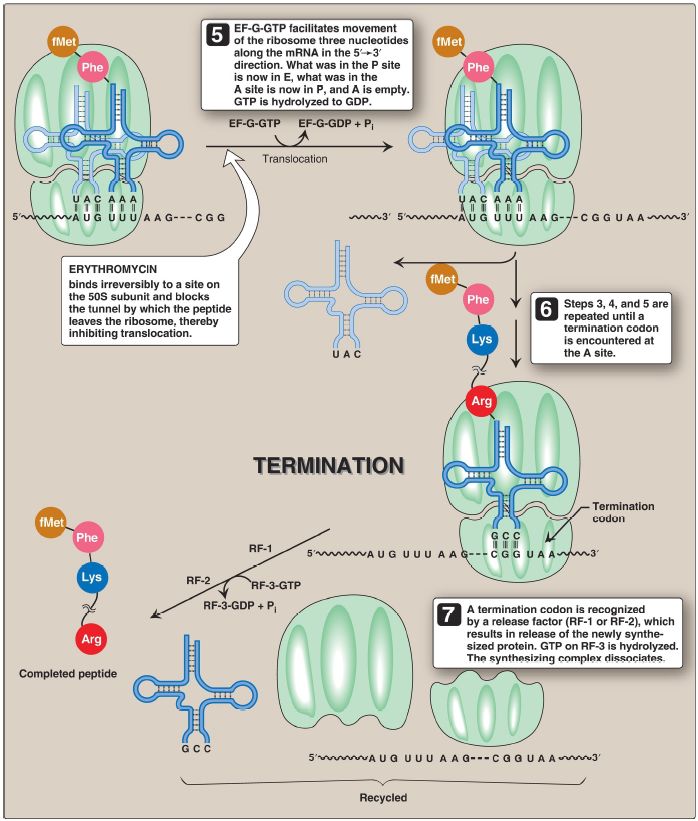
Figure 1 : Steps in prokaryotic protein synthesis (translation), and their inhibition by antibiotics. [Note: EF-Ts is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor. It facilitates the removal of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) from EF-Tu, allowing its replacement by guanosine triphosphate (GTP). The eukaryotic equivalent is EF-1βγ.] fMet = formylated methionine; S = Svedberg unit; Phe = phenylalanine; Lys = lysine; Arg = arginine; tRNA = transfer RNA; mRNA = messenger RNA.Figure 32.13(continued from previous page)[Note: In eukaryotes, diphtheria toxin inactivates EF-2, thereby inhibiting the translocation phase of elongation. Ricin, a toxin from castor beans, removes a specific A from the 28S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) in the large subunit of eukaryotic ribosomes, thereby inhibiting ribosomal function.]

Figure 2: Protein factors in the three stages of translation. = prokaryotes; =eukaryotes; tRNA = transfer RNA; IF = initiation factor; EF = elongation factor; RF = release factor; GTP = guanosine triphosphate.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


