

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The Leaving Group
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
الجزء والصفحة:
........
5-1-2022
2866
The Leaving Group
The reactivity of a given alkyl derivative, RX, in either SN1 or SN2 reactions, is influenced strongly by the leaving group, X. The choice of leaving group is therefore an important consideration in any synthesis involving SN reactions.
From the foregoing discussion of structural effects in the R group on SN reactivity, particularly in SN1 reactions, we might expect the stability of :X as an ion or neutral molecule to play a major role in determining how good or poor X is as a leaving group. The stability of :X is indeed important - the problem is that there are several factors that contribute to the stavility and hence the lability of the leaving group.
For the purpose of initially identifying good and poor leaving groups, consider development of a practical synthesis of diethyl ether. One route is by way of SN2 displacement using an ethyl compound, CH3CH2X, and ethoxide ion:
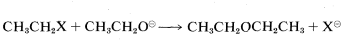
Many CH3CH2X compounds have X groups that are quite unsatisfactory in this reaction. They include compounds such as ethane, propane, ethanol, ethyl methyl ether, ethylamine, and ethyl ethanoate; the respective groups, H⊖, CH3⊖, HO⊖, CH3O⊖, NH2⊖, and CH3CO2⊖ all can be classified as very poor leaving groups. The more reactive ethyl derivatives (see Table 8-3) include the halides, particularly ethyl iodide, and sulfonic acid derivatives; the corresponding anions Cl⊖, Br⊖, I⊖, and RS(O2)O⊖ therefore are moderate to good leaving groups. Table 8-3 includes pertinent data for the rates of ether formation from various alkyl compounds and illustrates that the relative abilities of groups to leave are about the same in SN1 reactions as they are in SN2 reactions.
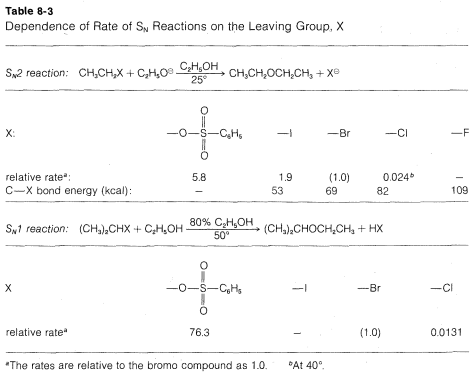
Why are groups such as I⊖ and RSO⊖ good leaving groups, whereas others such as H⊖, HO⊖ and NH2⊖ are poor? The simplest correlation is with the strength of HX as an acid. This is very reasonable because the ease of loss of X⊖, as from (CH3)C−X in an SN1 reaction, would be expected to be related, to some degree at least, to the ease of ionization of H−X to H⊕ and X⊖. Therefore the stronger HXHX is as an acid, the better X will be as a leaving group. Thus HFHF is a relatively weak acid and F⊖ is not a very good leaving group; H−I is a very strong acid and I⊖ is a good leaving group. The usual order of reactivity of alkyl halides, R−I > R−Br > R−Cl > R−F (when R is the same group throughout), is in accord with the acid strengths of the halogen acids. SImilarly, CF3CO2− is a much better leaving group than CH3CO2−, and we find that trifluoroethanoic acid, CF3CO2H is a several thousand times stronger acid than ethanoic acid, CH3CO2H. For the same reason, CF3SO3⊖ is a better leaving group than CH3XO3⊖.
This correlation can be extended easily to groups that leave as neutral X:. For example, ROH2⊕→R⊕+H2O occurs far more readily than ROH→R⊕+OH⊖ and we know that H3O⊕ is a stronger acid (or better proton donor) than H2O.
The relationship between X⊖ as a leaving group and HX as an acid is very useful because much information is available on acid strengths. However, it is not a very fundamental explanation unless we can explain why some acids are strong acids and others are weak acids. One factor is the strength of the H−X bond, but here we need to remember that the usual bond strengths are for dissociation to radicals or atoms, not ions, and for the gas, not for solutions. If we write the steps relating the bond-dissociation energy to the energy of ionic dissociation in solution, we see that for variations in X, in addition to the bond energy, the electron affinity of X⋅, the solvation energy of X⊖, and the solvation energy of HX, also will be contributing factors.
Figure 8-5 and Table 8-3).
Figure 8-5: Plot of C−X bond energies against H−X bond energies, using the data of Table 4-3
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















