


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
أقرأ أيضاً
التاريخ: 2025-01-08
التاريخ: 18-9-2019
التاريخ: 19-2-2017
التاريخ: 20-12-2015
|
The conditions used for substitution reactions by the SN2 mechanism very often lead to elimination. The reaction of 2-bromopropane with sodium ethoxide in ethanol provides a good example:
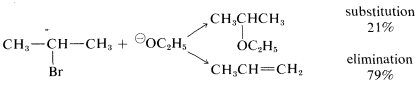
Elimination to give propene competes with substitution to give ethyl isopropyl ether. Furthermore, the rate of elimination, like the rate of substitution, is proportional to the concentrations of 2-bromopropane and ethoxide ion. Thus elimination here is a second-order reaction (it may be helpful to review Section 8-4 at this point):
rate of substitution =kS[RBr][⊖OC2H5]
rate of elimination =kE[RBr][⊖OC2H5]
As to the mechanism of this kind of elimination, the attacking base, ⊖OC2H5, removes a proton from the β carbon more or less simultaneously with the formation of the double bond and the loss of bromide ion from the neighboring carbon:
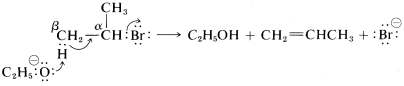
The abbreviation for this mechanism is E2, E for elimination and 2 for bimolecular, there being two reactants involved in the transition state.



|
|
|
|
مقاومة الأنسولين.. أعراض خفية ومضاعفات خطيرة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمل جديد في علاج ألزهايمر.. اكتشاف إنزيم جديد يساهم في التدهور المعرفي ؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تقيم ندوة علمية عن روايات كتاب نهج البلاغة
|
|
|