

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The Relation of NMR to Other Kinds of Spectroscopy
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
الجزء والصفحة:
........
11-1-2022
2377
The Relation of NMR to Other Kinds of Spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy involves transitions between possible energy levels of magnetic nuclei in an applied magnetic field (see Figure 9-21). The transition energies are related to the frequency of the absorbed radiation by the familiar equation ΔE−hνΔ. An important difference between nmr and other forms of spectroscopy is that ΔE is influenced by the strength of the applied field. This should not be surprising, because if we are to measure the energy of changing the direction of alignment of a magnetic nucleus in a magnetic field, then the stronger the field the more energy will be invloved.
Nuclear spin (symbolized as I) is a quantized property that correlates with nuclear magnetism such that when I is zero the nucleus has no spin and no magnetic properties. Examples are 12C and 16O. Several nuclei of particular interest to organic chemists - 1H, 13C, 15, 19, and 31P - have spin of 1/2. With I=1/2 there are only two magnetic energy states of the nucleus in a magnetic field. These states are designated with the spin quantum numbers +1/2 and −1/2. The difference in energy between these states, ΔE, is given by
or
in which h is Planck's constant, ν is in hertz, γ is a nuclear magnetic constant called the gyromagnetic ratio,10, and H is the magnetic field strength at the nucleus. In general, H will not be exactly equal to Ho, the applied magnetic field and, as we will see, this difference leads to important chemical information. Each kind of nucleus (1H, 13C, 15N, etc.) has its own γ value and, consequently, will undergo transitions at different frequencies at any particular value of H. This should become clearer by study of Figure 9-24.
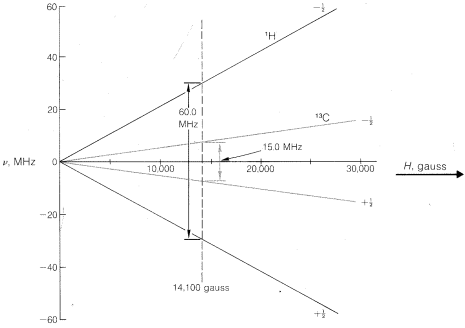
There are several modes of operation of an nmr spectrometer. First and most common, we hold νν constant and vary (or "sweep") HoHo. Close to ν=γH , energy is absorbed by the nuclei and the current flow from the transmitter increases until ν is exactly equal to γH. Further increase of HoHo makes ν<γHo and the current flow decreases. The form of the energy-absorption curve as a function of Ho when Ho is changed very slowly is shown in Figure 9-25a. The peak is centered on the point where ν=γH. When Ho is changed more rapidly, transient effects are observed on the peak, which are a consequence of the fact that the nuclei do not revert instantly from the −1/2 to +1/2 state. The resulting
Figure 9-25: Comparison of sweep rates on nmr absorption curves; (a) 500-sec sweep, (b) 50-secsec , (c) 10-sec sweep, The "ringing" in the faster sweep curves is a transient effect that has a small effect on the position of the peak and none on the integral.
phenomenon is called "ringing" and is shown in Figures 9-25b and 9-25c. Evidence of ringing also will be seen on peaks of Figure 9-23.
An alternative method of running an nmr spectrometer is to hold the magnetic field constant and to sweep the transmitter frequency through the resonances. This mode of operation is more like other forms of spectroscopy and gives the same line shapes as sweeping the field (Figure 9-25).
What energy is associated with a 1H nmr transition? The magnitude of this energy may be calculated from the relationship between energy and wavelength (frequency) of the absorbed radiation. That is,
The frequency ν is the operating frequency of the spectrometer, which we will take as 60MHz or 6×107 Hz (cycles sec−1), and the velocity of light is 3×108 m sec−1. Hence
This is a very small energy difference, which means that only very few more of the nuclei are in the more stable +1/2 state than in the less stable −1/2 state. The equilibrium constant K for −1/2⇌+1/2 calculated from Equation 4-2 for 25o and neglecting possible entropy effects is 1.000010!
 الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















