
Effects of Carbon Bond Type
 المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
 المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
 الجزء والصفحة:
........
الجزء والصفحة:
........
 13-1-2022
13-1-2022
 2838
2838
Effects of Carbon Bond Type
The shifts of the protons of alkanes and cycloalkanes fall in the range of 0.9-1.5ppm with C−H protons coming at the low-field end of this range and −CH3 protons coming at the high-field end ( Table 9-4).
Alkenic hydrogens (vinyl hydrogens, 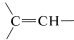 ) normally are observed between 4.6-6.3ppm toward lower fields than the shifts of protons in alkanes and cycloalkanes. This means that alkenic hydrogens in an organic compound can be easily distinguished from alkane hydrogens.
) normally are observed between 4.6-6.3ppm toward lower fields than the shifts of protons in alkanes and cycloalkanes. This means that alkenic hydrogens in an organic compound can be easily distinguished from alkane hydrogens.
Aromatic protons, such as those in benzene, have shifts at still lower fields and commonly are observed at 7-8 ppm. In contrast, alkynic protons of the type −C≡CH give resonances that are upfield of alkenic or aromatic protons and come at 2-3ppm. Another effect associated with multiple bonds is the large difference in shift between a −CH(OCH3)2 proton, which normally comes at about 5.5ppm, and aldehyde protons, −CH=O, which are much farter downfield at 9-11ppm.
Clearly, the shifts of a proton depend on whether the carbon forms single, double, or triple bonds. In a magnetic field, the circulation of electrons in the π orbitals of multiple bonds induced by the field (Figure 9-26) generates diamagnetic shielding effects in some regions of the multiple bond and paramagnetic deshielding effects in other regions. Apparently, protons attached to double-bonded carbons are in the deshielding zones and thus are downfield while protons attached to triple-bonded carbons are in the shielding zones and are observed at rather high field.
 الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


