
Why Antarafacial Addition?
 المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
 المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
 الجزء والصفحة:
........
الجزء والصفحة:
........
 14-1-2022
14-1-2022
 2869
2869
Why Antarafacial Addition?
The simple carbocation intermediate of Equation 10-1 does not account for formation of the antarafacial-addition product. The results with SN1 reactions and the atomic-orbital representation predict that the bonds to the positively charged carbon atom of a carbocation should lie in a plane. Therefore, in the second step of addition of bromine to cycloalkenes, bromide ion could attack either side of the planar positive carbon to give a mixture of cis- and trans-1,2-dibromocyclohexanes. Nonetheless, antarafacial addition occurs exclusively:
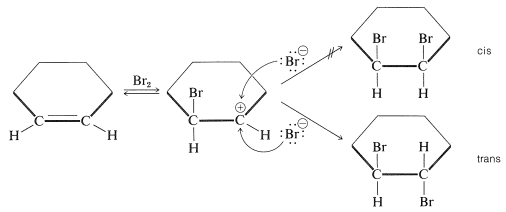
To account for the stereospecificity of bromine addition to alkenes, it has been suggested that in the initial electrophilic attack of bromine a cyclic intermediate is formed that has bromine bonded to both carbons of the double bond. Such a "bridged" ion is called a bromonium ion because the bromine formally carries the positive charge:
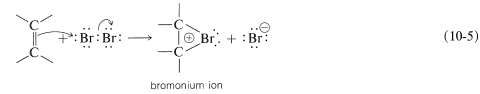
An SN2-type of attack of bromide ion, or other nucleophile, at carbon on the side opposite to the bridging group then results in formation of the antarafacial-addition product:
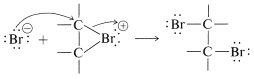
We may seem to have contradicted ourselves because Equation 10-1 shows a carbocation to be formed in bromine addition, but Equation 10-5 suggests a bromonium ion. Actually, the formulation of intermediates in alkene addition reactions as "open" ions or as cyclic ions is a controversial matter, even after many years of study. Unfortunately, it is not possible to determine the structure of the intermediate ions by any direct physical method because, under the conditions of the reaction, the ions are so reactive that they form products more rapidly than they can be observed. However, it is possible to generate stable bromonium ions, as well as the corresponding chloronium and iodonium ions. The technique is to use low temperatures in the absence of any strong nucleophiles and to start with a 1,2-dihaloalkane and antimony pentafluoride in liquid sulfur dioxide:
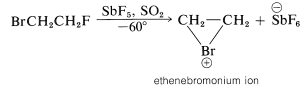
The C2H4Br⊕ ions produced in this way are relatively stable and have been shown by nmr to have the cyclic halonium ion structure.
 الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


