
The Lorentz transformation
 المؤلف:
Richard Feynman, Robert Leighton and Matthew Sands
المؤلف:
Richard Feynman, Robert Leighton and Matthew Sands
 المصدر:
The Feynman Lectures on Physics
المصدر:
The Feynman Lectures on Physics
 الجزء والصفحة:
Volume I, Chapter 15
الجزء والصفحة:
Volume I, Chapter 15
 2024-02-15
2024-02-15
 1963
1963
When the failure of the equations of physics in the above case came to light, the first thought that occurred was that the trouble must lie in the new Maxwell equations of electrodynamics, which were only 20 years old at the time. It seemed almost obvious that these equations must be wrong, so the thing to do was to change them in such a way that under the Galilean transformation the principle of relativity would be satisfied. When this was tried, the new terms that had to be put into the equations led to predictions of new electrical phenomena that did not exist at all when tested experimentally, so this attempt had to be abandoned. Then it gradually became apparent that Maxwell’s laws of electrodynamics were correct, and the trouble must be sought elsewhere.
In the meantime, H. A. Lorentz noticed a remarkable and curious thing when he made the following substitutions in the Maxwell equations:
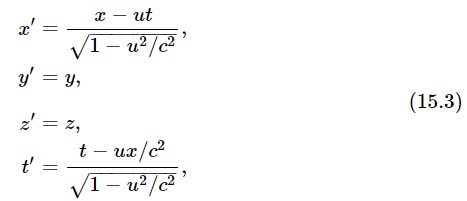
namely, Maxwell’s equations remain in the same form when this transformation is applied to them! Equations (15.3) are known as a Lorentz transformation. Einstein, following a suggestion originally made by Poincaré, then proposed that all the physical laws should be of such a kind that they remain unchanged under a Lorentz transformation. In other words, we should change, not the laws of electrodynamics, but the laws of mechanics. How shall we change Newton’s laws so that they will remain unchanged by the Lorentz transformation? If this goal is set, we then have to rewrite Newton’s equations in such a way that the conditions we have imposed are satisfied. As it turned out, the only requirement is that the mass m in Newton’s equations must be replaced by the form shown in Eq. (15.1). When this change is made, Newton’s laws and the laws of electrodynamics will harmonize. Then if we use the Lorentz transformation in comparing Moe’s measurements with Joe’s, we shall never be able to detect whether either is moving, because the form of all the equations will be the same in both coordinate systems!
It is interesting to discuss what it means that we replace the old transformation between the coordinates and time with a new one, because the old one (Galilean) seems to be self-evident, and the new one (Lorentz) looks peculiar. We wish to know whether it is logically and experimentally possible that the new, and not the old, transformation can be correct. To find that out, it is not enough to study the laws of mechanics but, as Einstein did, we too must analyze our ideas of space and time in order to understand this transformation. We shall have to discuss these ideas and their implications for mechanics at some length, so we say in advance that the effort will be justified, since the results agree with experiment.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


