


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيويةBiotin
Biotin is a vitamin (vitamin H) and a growth factor, first isolated by Kögl in 1935 (1). Its structure ) Fig. 1) was established by du Vigneaud in 1942 (2, 3).
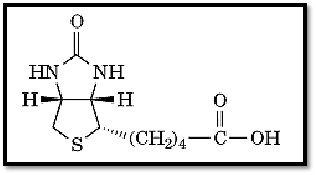
Figure 1. The structure of biotin.
Biotin is a prosthetic group for a family of “biotin-requiring” enzymes (carboxylases, decarboxylases and transcarboxylases) (4). These multisubunit enzymes contain two types of active sites, one wherein a molecule containing a carboxylic acid group serves as a donor of the carboxyl group and the second wherein another molecule acts as an acceptor. The biotin moiety is attached through a lysine residue in a particular sequence (Ala-Met-Lys-Met) that is exposed on the surface of a special type of biotin-binding subunit. The biotin group participates as a transient carrier to which the carboxyl group is bound covalently in the process of being transferred from the donor to the acceptor molecule. The biotin moiety of the enzyme is readily available for binding to avidin, which inactivates the enzyme. After serving their respective function, the biotin-requiring enzymes undergo degradation, whereby e-N-biotinyl lysine (termed biocytin) is released into the circulation. There the enzyme biotinidase hydrolyzes biocytin to regenerate biotin and lysine. A rare mutation in the gene in humans causes a deficiency in the level of this enzyme in the blood stream, which, in turn, causes a disease due to a deficiency of biotin (5).
Biotin attained true fame when it was recognized that the high-affinity interaction between avidin and biotin can be applied for a variety of biotechnological and biomedical purposes (as described in Avidin-biotin system)(6, 7). The varied application of this system is usually achieved upon coupling biotin covalently to different biologically active binder molecules, antibodies, hormones, DNA, etc. The binding of biotin to either avidin or streptavidin greatly enhances the stability of these proteins, such that the avidin–biotin or streptavidin–biotin complex is essentially irreversible. Because both proteins primarily recognize the ureido ring of the biotin molecule, the carboxylic acid side-chain can be modified almost at will, and the resultant derivatives can be used to incorporate biotin covalently into virtually any other molecule (Fig. 2).
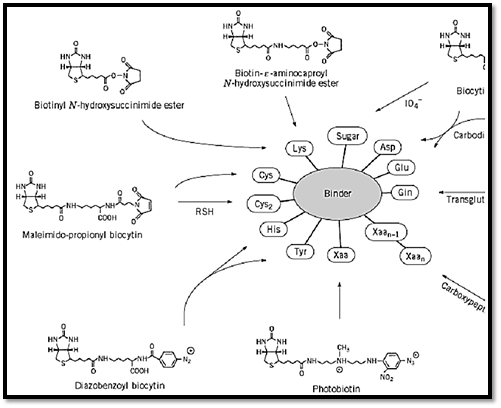
Figure 2. Selected approaches using different biotin-containing reagents for biotinylating functional groups on proteins.
Both polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies have been produced against biotin. Comparing the sequence of the VH region of a monoclonal anti-biotin preparation (8) with the sequences of avidin and streptavidin revealed an astonishing similarity in their binding sites, indicating that such functional elements are conserved in nature for a given purpose, irrespective of the protein type.
References
1.F. Kögl and B. Z. Tönnis (1936) Physiol. Chem. 242, 43–73.
2. V. du Vigneaud, D. B. Melville, K. Folkers, D. E. Wolf, R. Mozingo, J. C. Kereszteolf, and S. A. Harris (1942) J. Biol. Chem. 146, 475–485.
3.V. du Vigneaud, K. Hoffman, and D. B. Melville (1942) J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 64, 188–189.
4.J. Moss and M. D. Lane (1971) Adv. Enzymol. 35, 321–372.
5.B. Wolf, G. S. Heard, J. R. McVoy, and R. E. Grier (1985) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 447, 252–62.
6.E. A. Bayer and M. Wilchek (1978) Trends Biochem. Sci. 3, N237–N239.
7.E. A. Bayer and M. Wilchek (1980) Methods Biochem. Anal. 26, 1–45.
8. H. Bagci, F. Kohen, U. Kuscuoglu, E. A. Bayer, and M. Wilchek (1993) FEBS Lett. 322, 47–50.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
باحثة تفتح الباب على ملف انتهاكات حقوق الإنسان في العراق ودور العدالة الانتقالية
|
|
|