

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Four-Membered Rings
المؤلف:
المصدر:
الجزء والصفحة:
21-12-2015
2941
Four-Membered Rings
Preparation
Several methods of preparing four-membered heterocyclic compounds are shown in the following diagram. The simple procedure of treating a 3-halo alcohol, thiol or amine with base is generally effective, but the yields are often mediocre. Dimerization and elimination are common side reactions, and other functions may compete in the reaction. In the case of example 1, cyclization to an oxirane competes with thietane formation, but the greater nucleophilicity of sulfur dominates, especially if a weak base is used. In example 2 both aziridine and azetidine formation are possible, but only the former is observed. This is a good example of the kinetic advantageof three-membered ring formation. Example 4 demonstrates that this approach to azetidine formation works well in the absence of competition. Indeed, the exceptional yield of this product is attributed to the gem-dimethyl substitution, the Thorpe-Ingold effect, which is believed to favor coiled chain conformations. The relatively rigid configuration of the substrate in example 3, favors oxetane formation and prevents an oxirane cyclization from occurring. Finally, the Paterno-Buchi photocyclizations in examples 5 and 6 are particularly suited to oxetane formation.
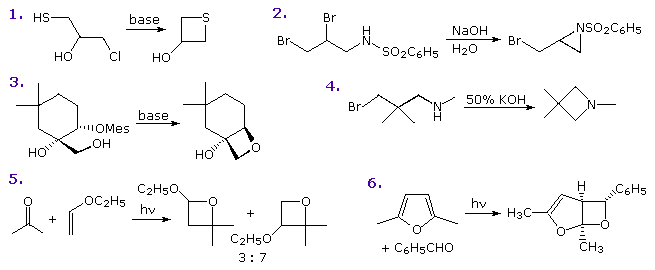
Reactions
Reactions of four-membered heterocycles also show the influence of ring strain. Some examples are given in the following diagram. Acid-catalysis is a common feature of many ring-opening reactions, as shown by examples 1, 2 & 3a. In the thietane reaction (2), the sulfur undergoes electrophilic chlorination to form a chlorosulfonium intermediate followed by a ring-opening chloride ion substitution. Strong nucleophiles will also open the strained ether, as shown by reaction 3b. Cleavage reactions of β-lactones may take place either by acid-catalyzed acyl exchange, as in 4a, or by alkyl-O rupture by nucleophiles, as in 4b. Example 5 is an interesting case of intramolecular rearrangement to an ortho-ester. Finally, the β-lactam cleavage of penicillin G (reaction 6) testifies to the enhanced acylating reactivity of this fused ring system. Most amides are extremely unreactive acylation reagents, thanks to stabilization by p-π resonance. Such electron pair delocalization is diminished in the penicillins, leaving the nitrogen with a pyramidal configuration and the carbonyl function more reactive toward nucleophiles.
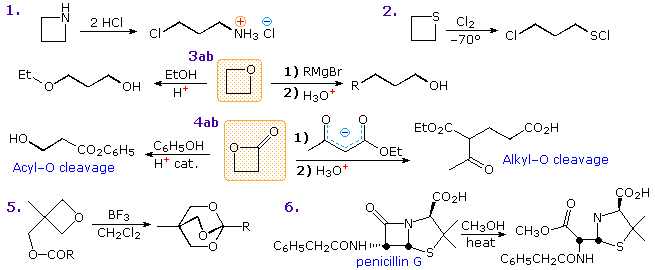
Reference
http://www2.chemistry.msu.edu/faculty/reusch/VirtTxtJml/heterocy.htm#top1
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















