
Effective nuclear charge and Slater’s rules Slater’s rules
 المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
 المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
p19
الجزء والصفحة:
p19
 11-2-2016
11-2-2016
 4958
4958
Effective nuclear charge and Slater’s rules Slater’s rules
Effective nuclear charges, Zeff, experienced by electrons in different atomic orbitals may be estimated using Slater’s rules. These rules are based on experimental data for electron promotion and ionization energies, and Zeff is determined from the equation.
Zeff= Z = S, where Z = nuclear charge, Zeff = effective nuclear charge, S = screening (or shielding) constant.
Values of S may be estimated as follows.
1. Write out the electronic configuration of the element in the following order and groupings. (1s), (2s, 2p),
(3s, 3p), (3d ), (4s, 4p), (4d ), (4f ), (5s, 5p) etc.
2. Electrons in any group higher in this sequence than the electron under consideration contribute nothing to S.
3. Consider a particular electron in an ns or np orbital.
(i) Each of the other electrons in the (ns, np) group
contributes S = 0.35.
(ii) Each of the electrons in the (n - 1) shell contributes
S = 0.85.
(iii) Each of the electrons in the (n - 2) or lower shells contributes S = 1.00.
4. Consider a particular electron in an nd or nf orbital.
(i) Each of the other electrons in the (nd, nf ) group contributes S = 0.35.
(ii) Each of the electrons in a lower group than the one being considered contributes S = 1.00.
An example of how to apply Slater’s rules
Question. Confirm that the experimentally observed electronic
configuration of K, 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1, is energetically more stable than the configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d1. For K, Z = 19.
Applying Slater’s rules, the effective nuclear charge experienced by the 4s electron for the configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 is.
Zeff = Z = S = 19 –[(8 - 0.85) + (10 - 1.00) = 2.20
The effective nuclear charge experienced by the 3d electron for the configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d1 is.
Zeff = Z = S
= 19 –[(18 -1.00) = 1.00
Thus, an electron in the 4s (rather than the 3d) atomic orbital is under the influence of a greater effective nuclear charge and in the ground state of potassium, it is the 4s atomic orbital that is occupied.
Slater versus Clementi and Raimondi values of Zeff Slater’s rules have been used to estimate ionization energies, ionic radii and electronegativities. More accurate effective nuclear charges have been calculated by Clementi and Raimondi by using self-consistent field (SCF) methods, and indicate much higher Zeff values for the d electrons.
However, the simplicity of Slater’s approach makes this an attractive method for ‘back-of-the-envelope’ estimations of Zeff. the periodic table has been extensively modified, and it is now recognized that periodicity is a consequence of the variation in ground state electronic configurations. A modern periodic table (Figure 1.) emphasizes the blocks of 2, 6, 10 and 14 elements which result from the filling of the s, p, d and f atomic orbitals respectively. An exception is He, which, for reasons of its chemistry, is placed in a group with Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe and Rn. A more detailed periodic table is given inside the front cover of the book.
The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) has produced guidelines for naming blocks and groups of elements in the periodic table. In summary, . blocks of elements may be designated by use of the letters s, p, d or f (Figure 1.);
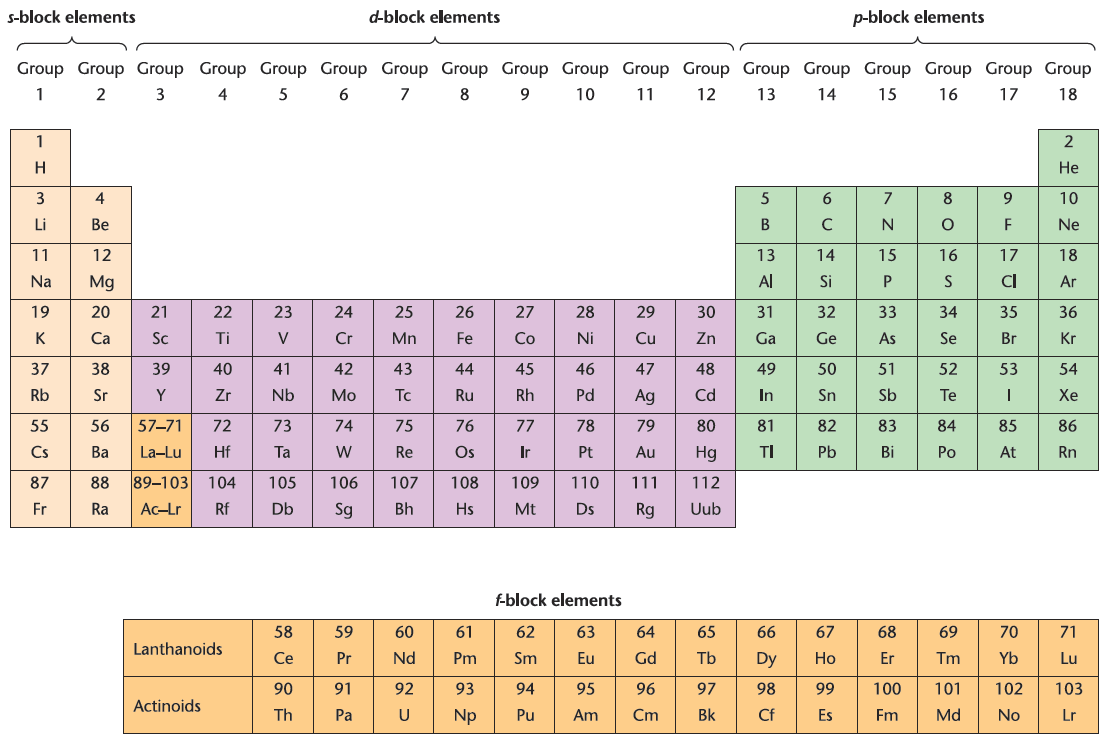
Fig. 1. The modern periodic table in which the elements are arranged in numerical order according to the number of protons (and electrons) they possess. The division into groups places elements with the same number of valence electrons into vertical columns within the table. Under IUPAC recommendations, the groups are labelled from 1 to 18 . The vertical groups of three d-block elements are called triads. Rows in the periodic table are called periods.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


