
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Spectral Line Emissions from Atoms and Molecules
المؤلف:
Diane Fisher Miller
المصدر:
Basics of Radio Astronomy
الجزء والصفحة:
p23
25-2-2016
2681
Spectral Line Emissions from Atoms and Molecules
While the mechanism behind thermal-related energy emissions from ionized gases involves electrons becoming detached from atoms, line emissions from neutral hydrogen and other atoms and molecules involves the electrons changing energy states within the atom, emitting a photon of energy at a wavelength characteristic of that atom. Thus, this radiation mechanism is called line emission, since the wavelength of each atom occupies a discrete “line” on the electromagnetic spectrum.
In the case of neutral (not ionized) hydrogen atoms, in their lower energy (ground) state, the proton and the electron spin in opposite directions. If the hydrogen atom acquires a slight amount of energy by colliding with another atom or electron, the spins of the proton and electron in the hydrogen atom can align, leaving the atom in a slightly excited state. If the atom then loses that amount of energy, it returns to its ground state. The amount of energy lost is that associated with a photon of 21.11 cm wavelength (frequency 1428 MHz).
Formation of the 21-cm Line of Neutral Hydrogen
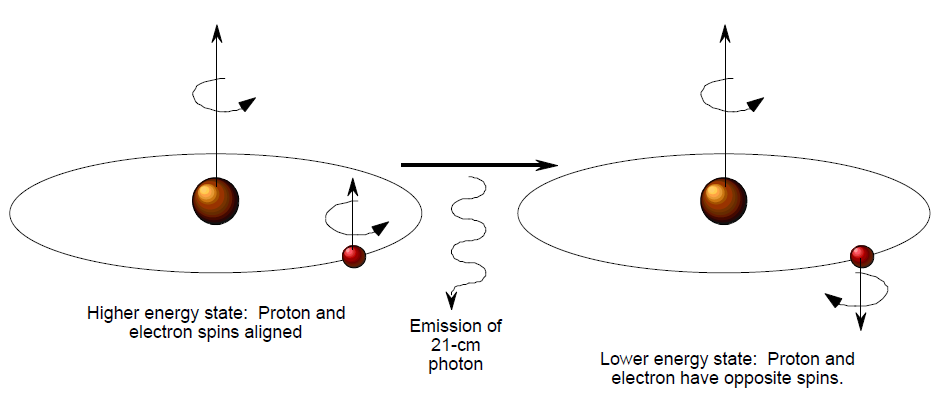
Hydrogen is the key element in the universe. Since it is the main constituent of interstellar gas, we often characterize a region of interstellar space as to whether its hydrogen is neutral, in which case we call it an H I region, or ionized, in which case we call it an H II region.
Some researchers involved in the search for extra-terrestrial intelligence have reasoned that another intelligent species might use this universal 21-cm wavelength line emission by neutral hydrogen to encode a message; thus these searchers have tuned their antennas specifically to detect modulations to this wavelength. But, perhaps more usefully, observations of this wavelength have given us much information about the interstellar medium and locations and extent of cold interstellar gas.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















