
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Horizon Coordinate System
المؤلف:
Diane Fisher Miller
المصدر:
Basics of Radio Astronomy
الجزء والصفحة:
p66
3-3-2016
2852
Horizon Coordinate System
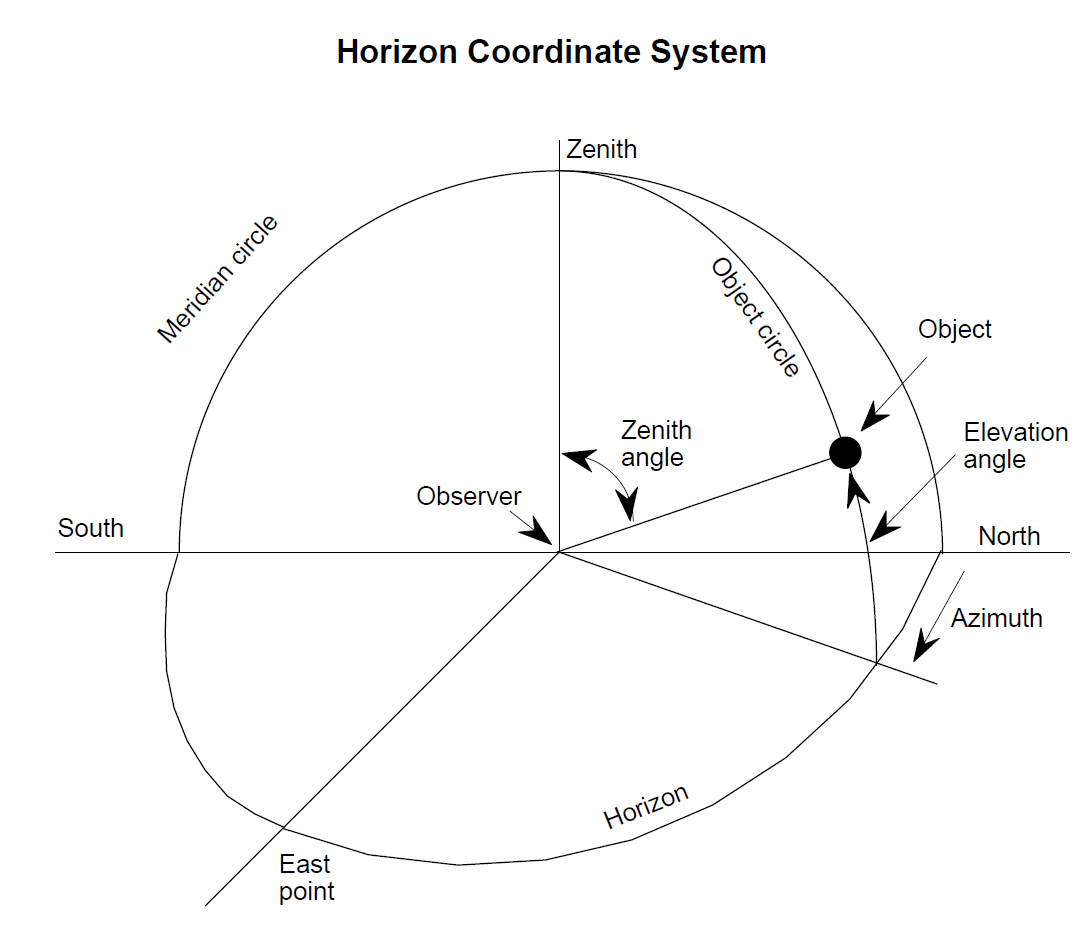
The horizon is defined as the dividing line between the Earth and the sky, as seen by an observer on the ground. In the horizon coordinate system the astronomical horizon is the hypothetical interface between Earth and sky, as would be seen by the observer if the surrounding terrain were perfectly flat (as out on a calm ocean).
Referring to the drawing below, zenith is the point straight overhead, perpendicular to the horizon plane, and nadir is the point directly under the observer. A vertical circle through an object in the sky and the zenith is the object circle. The coordinates of the object are given by the azimuth, which is the horizontal angle from north clockwise to the object circle, and the altitude or elevation angle, which is measured upward from the horizon to the object. The great circle through the north and south points on the horizon and the zenith is called the meridian.
A horizon mask is a diagram that maps in silhouette the horizon in 360° of azimuth as actually seen by the observer, including hills, valleys, mountains, buildings, trees, and anything else that would hide from view any part of the sky that would be visible if the terrain were perfectly flat. A horizon mask for the GAVRT is shown on the next page.
In the horizon system, the coordinates of an object in the sky change throughout the day with Earth’s rotation. While the azimuth and elevation angles are convenient for positioning a radio telescope antenna that rotates around horizontal and vertical axes (AZ-EL mounted), they are not so convenient for specifying the position of a celestial object. Better for this purpose are systems using fixed coordinates, such as the equatorial coordinate system.

 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















