
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Uniform Acceleration
المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
p 44
13-10-2016
713
Uniform Acceleration
Suppose an object starts at rest with respect to the lab frame and undergoes a uniform acceleration a′ as measured by an observer on a spaceship moving at a uniform velocity v with respect to the lab. In Newtonian mechanics, for speeds where v << c, the velocity after t ′ seconds in the moving frame has elapsed is V′ = a′ t ′ as measured by the observer on the moving object. This velocity is V = v + a′ t after the elapsed time t in the lab frame, because in Newtonian physics the clocks in the different frames run at the same rates. What is the velocity value in the lab frame when the speed is allowed to become relativistic? Can the product at be greater than c in either reference frame?
Answer
In the STR, the velocity in the lab frame is no longer V = a′t for a uniform acceleration a′ in the moving frame. However, in the moving frame at each instant the expression V′ = a′t ′ continues to be true. To convert from the moving frame to the lab frame, we must essentially convert the clock readings and time interval using dt/dτ 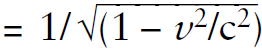 . Here, τ is the proper time that is, the clock reading on a wristwatch worn by an observer on the spaceship, say, and dτ is the proper time interval between two events at the same location. In the example, τ is the elapsed time on the wristwatch of the person on the moving frame. Hence, on the moving spaceship frame, V′ = a′τ.
. Here, τ is the proper time that is, the clock reading on a wristwatch worn by an observer on the spaceship, say, and dτ is the proper time interval between two events at the same location. In the example, τ is the elapsed time on the wristwatch of the person on the moving frame. Hence, on the moving spaceship frame, V′ = a′τ.
Before we determine the answer for the velocity of the object in the lab frame, let’s review the simpler problem of how velocities are added in relativistic frames. If an object moves forward with the velocity V′ in the spaceship frame, then the object’s velocity V in the lab frame is determined by the law of addition of velocities V/c = (V′/c + Vs/c)/(1 + V′Vs/c2), where Vs is the uniform velocity of the spaceship in the lab frame. One can check the limiting case for low velocities, when V′Vs/c2 is very small, to verify agreement with Galilean relativity that is, the two velocities simply add. To relate the acceleration of the object as seen by both observers, the addition of velocities expression is differentiated with respect to the time in the lab reference frame to obtain a = a′ /{(1 + V′Vs/c2) 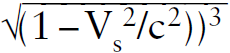 }, a messy expression. The velocity of the accelerating object in the lab frame is found by substituting V′ = a′ τ. Therefore a ≠ a′ and V < c.
}, a messy expression. The velocity of the accelerating object in the lab frame is found by substituting V′ = a′ τ. Therefore a ≠ a′ and V < c.
An alternative mathematical technique using a velocity parameter defined in terms of hyperbolic functions is given in the Taylor and Wheeler reference below.
 الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















