
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Bragg Scattering of X-rays
المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
p 80
26-10-2016
640
Bragg Scattering of X-rays
Bragg scattering of X-rays of wavelength λ in an ideal crystal satisfies Bragg’s law: 2d sin θ = m λ, where d is the spacing between adjacent scattering planes and θ is the angle measured from the surface of the crystal, not the perpendicular. When this condition is met for various integer values of m, constructive interference from the entire family of parallel planes occurs because the path differences are integral multiples of the X-ray wavelength. One often reads that the Bragg scattering of X-rays from an ideal crystal is a coherent scattering process that is, all the Bragg-scattered X-rays arrive in phase at the detector. Why is it not so?
Answer
Bragg scattering requires λ < d; therefore there will not be any collective scattering from a group of scatterers at different atoms within one wavelength. The actual scatterers of the X-rays are the electrons at each atom in these planes of the crystal. Coherent scattering requires fixed phase relationships, but there is no fixed phase relationship between electrons at different atoms nor between the electrons doing the scattering at any moment. Therefore, the X-rays scattered into the Bragg angle have a multitude of random phases and not fixed-phase relationships. The scattering probability is proportional to N, the number of scatterers, and not N2 , as it would be for coherent scattering.
Here is the QM argument mathematically. Let ψi represent the probability amplitude to scatter an X-ray at the i th atom. We know from QM rule 2 that Ψ = ψ1 + ψ2 + ψ3 + . . . , for alternative ways to go from the X-ray source to the crystal to the X-ray detector. Each ψi represents one atom, and we assume single scatterings on the way to the detector for simplicity. Each ψi = exp[iδ] φi , which includes a phase part exp[iδ] and the identical scattering amplitude φi at the identical atoms in the crystal. If the phase part at each scattering atom is identical, then we would have Ψ = N ψ1 and the probability P = N2 |ψ1| 2, giving us coherent scattering proportional to N2.
However, there is no correlated motion between electrons on different atoms, so their phases are random. If the phase differences between scatterers that is, the electrons on different atoms are not fixed differences, then the sum is over random phases and, like the random walk problem, the total amount is proportional to 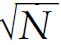 instead of N. Therefore Ψ =
instead of N. Therefore Ψ = 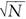 ψ1, so P = N |ψ1|2. The Bragg scattering of X-rays is not a coherent scattering process.
ψ1, so P = N |ψ1|2. The Bragg scattering of X-rays is not a coherent scattering process.
 الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















