
Nuclear Energy Levels
 المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
 المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 93
الجزء والصفحة:
p 93
 6-11-2016
6-11-2016
 745
745
Nuclear Energy Levels
In the 1930s and 1940s, physicists working on the energy states of the nucleus of an atom concentrated on various models, including a shell model using the Schrodinger equation with an approximately constant electrical potential inside the nucleus. Conceptually, each nucleon is in a well-defined orbit within the nucleus and moves in an averaged field produced by all the other nucleons. However, even though quantum
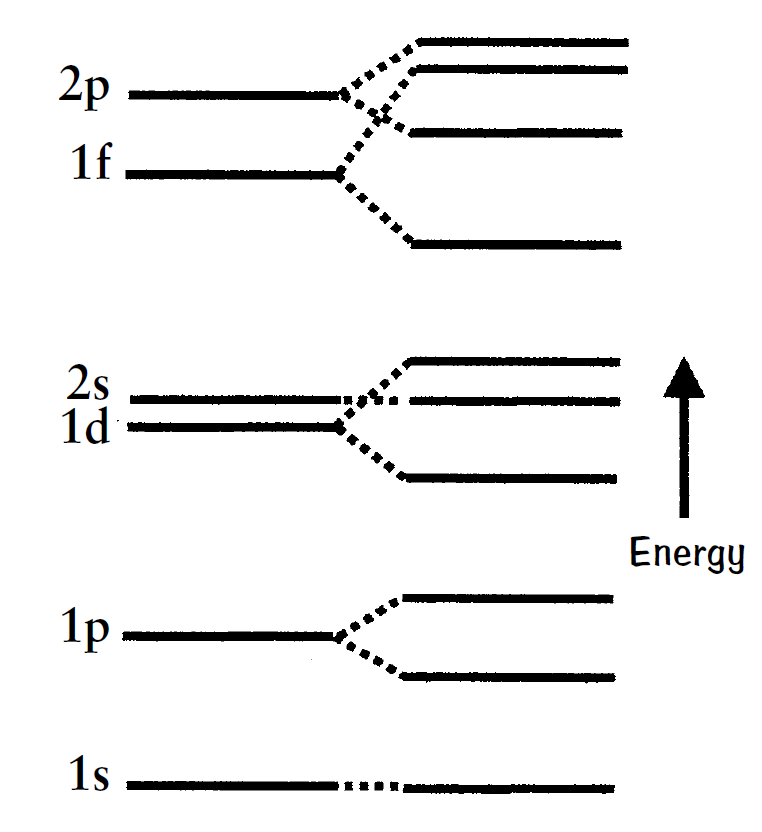
states such as n = 1, with l = 0, 1, 2, 3, etc., are possible in the shell model, the predicted energy levels did not fit the data. In fact, the actual energy levels were all scrambled compared to the shell-model theoretical predictions. Why?
Answer
Even the shell model, often called the independent particle model of the nucleus, fails to correctly predict many of the energy level spacings unless the spin-orbit LS interactions are included. That is, the proton and neutron magnetic moments interact with magnetic fields produced by their orbital motions. These LS interactions add terms to the approximate constant potential of the shell model to dominate the quantum state sequence inside the nucleus. As a result, many energy levels change their relative positions on the energy scale, with levels from different principle quantum numbers becoming interchanged! Once the LS interaction was properly accounted for, all its predictions were shown to agree with the empirical data.
This model of the nucleus also explained why nuclei containing an even number of protons and neutrons are more stable than others. Like the energy levels for the electrons in quantum states outside the nucleus, the Fermi exclusion principle allows two identical particles per quantum state only. The nuclear quantum states for the protons are separate from the nuclear quantum states for the neutrons, and any particular state is filled when there are two identical particles with opposite spins. The proton levels are higher in energy than the corresponding neutron levels because there is the added Coulomb repulsion. Any extra proton or neutron can be added, but this additional particle must occupy a higher energy state, usually leading to an unstable nucleus.
 الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


