

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Free Connective Tissue Cells-Plasma Cells
المؤلف:
Kuehnel, W
المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
الجزء والصفحة:
11-1-2017
1990
Free Connective Tissue Cells-Plasma Cells
Plasma cells are most frequently found in the cellular connective tissue of various organs (lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, lung, lamina propria of the intestinal mucosa). They are sporadically found in connective tissue every-where in the body, except in blood. They are abundant in areas with chronic inflammation. Plasma cells are round or polyhedral with rounded or oval nuclei, usually in an eccentric location. The chromatin structure is characteristic of these cells. Starting at the nucleolus, it extends to the inner nuclear membrane in a star-like fashion. Chromatin accumulates at the inner nuclear membrane. This creates the wheel-spoke nucleus, as seen in light microscopy. Plasma cells are remarkably rich in intracellular granular membrane systems ( ergastoplasm ), which account for the basophilia. The mem-branes of the rough (granular) endoplasmic reticulum (rER) organize in a pattern and form cisternae in some locations. Rough ER membranes are absent from the Golgi region in the cell center. Crista-type mitochondria are present in the cytoplasm as well. Plasma cells are the final stage in the B-lymphocyte series. They are local (fixed) cells and do not divide; their lifespan is 10–30 days. They synthesize antibodies (proteins), and their function therefore serves the humoral immune response. Antibodies are release d (by extrusion ) without the formation of secretor y granules. Plasma cell from a lung (cat).
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 17000

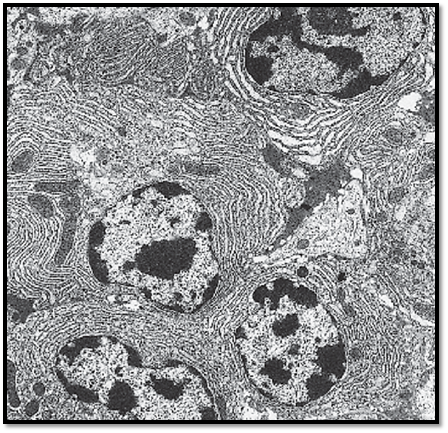
Free Connective Tissue Cells—Plasma Cells
Plasma cells from the loosely organized connective tissue from the orbital gland of a sparrow. The cells are close together and form a small group. Plasma cells, the final cells in the B-lymphocyte series, are large, either oval or round and usually have round nuclei with dense coarse heterochromatin. Their characteristic is the abundance of granular (rough) endoplasmic reticulum (rER) as a location for immunoglobulin synthesis. It explains the conspicuous basophilia in light microscopy . In the plasma cell in the top right part of the figure, the rER cisternae are distended. All cells contain mitochondria of different sizes.
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 9000
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .
 الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















