

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Descending Thoracic Aorta
المؤلف:
Kuehnel, W
المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
الجزء والصفحة:
15-1-2017
2912
Descending Thoracic Aorta
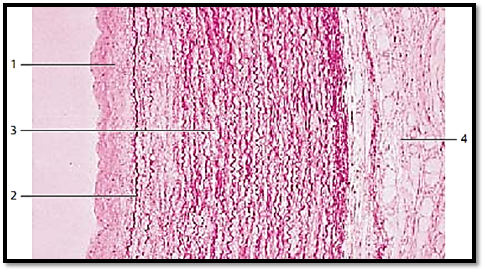
This cross-section of a thoracic aortic wall exemplifies a typical elastic artery. The tunica intima 1 , followed by the membrana elastica interna 2 adjoin the tunica media . The tunica me dia 3 consists of concentric layers of fenestrated elastic membranes, which are interspersed with myocytes, f ibrocytes, thin collagen fibrils and amorphous substances with a high chondroitin sulfate content. The undulating elastic f ibers stand out in vertical sections. Apart from collagen f ibers, the tunica adventitia 4 also contains elastic fibers, fibrocytes, adipocytes and vasa vasorum .
1 Tunica intima
2 Internal elastic membrane, membrana elastica interna
3 Tunica media
4 Tunica adventitia
Stain: hematoxylin-eosin-resorcin-fuchsin; magnification: × 80
Descending Thoracic Aorta
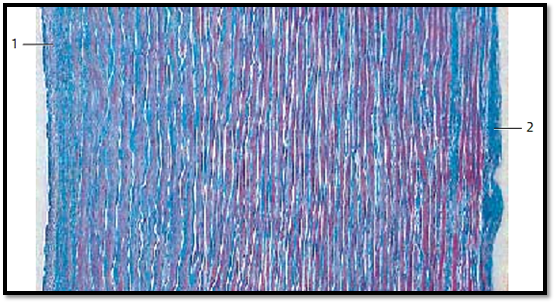
This section across the aortic wall gives a general impression of the number of components and their distribution: elastic membranes ( fenestrated mem-branes) are stained white. Collagen fibers appear blue and myocytes are stained red. The small, only lightly colored strip on the left represents the tunica intima 2 . The heavily stained band on the outer right is the tunica externa 1 . The tunica me dia makes up most of the wall. Note: the tunica me dia is not as clearly distinguishe d from the neighboring layers, as is the case for a typical muscular artery. The three-layer arrangement is blurred.
1 Tunica interna (intima)
2 Tunica externa (adventitia)
Stain: azan; magnification: × 50
Descending Thoracic Aorta
The descending aorta, being located close to the heart, is an elastic artery. Due to an abundance of elastic fibers, the aorta and other coronary arteries of elastic type show a yellowish tint, even on the macroscopic level. The elastic components pervade the entire wall. This obscures the borders between layers, which are unlike the distinct borders in muscular arteries. The elastic elements take the form of 30–70 concentric layers of fenestrated elastic membranes . Their structural details are accessible only in parallel cuts through the aortic wall. In this cross-section through the tunica media of the aortic wall, the elastic membranes appear as separate, sometimes undulating fibers . The elastic membranes alternate with thin layers of smooth muscle cells (yellow). The latter are tensor muscles and originate with the elastic matrix ( elastic muscular systems ). The nuclei have not been stained.
Stain: Weiger t’s resorcin-fuchsin-picric acid; magnification: × 200

Descending Thoracic Aorta
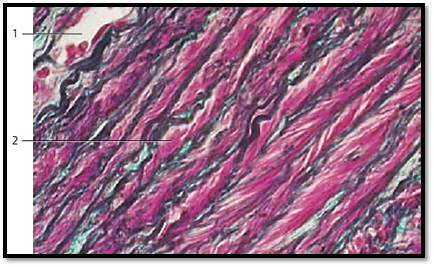
This cross-section of the tunica media from the descending aorta shows strong, in some places undulating elastic membranes (stained blue-violet). In a vertical section, they appear as fibers with intertwined muscle cells. At their insertion sites, the muscle fibers create the image of brush strokes. The myocytes encircle the aorta, forming right- and left-handed spirals. This creates a fishbone pattern in a cross-section. In this arrangement, the smooth muscle cells can regulate the tensile force of the elastic fiber network . The collagen connective tissue is stained green. A vessel of the vessel wall 1 ( vas vasis ) is visible in the left corner of the image.
1 Vessel with erythrocytes
2 Smooth muscle cells, myocytes
Stain: Masson-Goldner trichrome; magnification: × 400
Descending Thoracic Aorta
This parallel section shows the fiber network of the tunica media. It features strong lamellae, homogeneous layers of 2–3- μm thick elastic membranes as well as singular elastic f ib ers. They form tight concentric layers. The webbed membranes leave openings in different shapes and sizes and in this way, form fenestrated elastic membranes . The number of these fenestrate d elastic membranes increases with age (35–40 for a newborn, 65–75 for an adult). The wall muscles of elastic arteries regulate predominantly the tensile force of the elastic fiber network and, only to a lesser degree, the lumen of the artery.
Stain: Weiger t’s resorcin-fuchsin-picric acid; magnification: × 300

References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .
 الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















