
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Motion of ultrarelativistic particles
المؤلف:
Heino Falcke and Friedrich W Hehl
المصدر:
THE GALACTIC BLACK HOLE Lectures on General Relativity and Astrophysics
الجزء والصفحة:
p 135
2-2-2017
1844
Motion of ultrarelativistic particles
1.1 Equations of motion
When the energy E is much larger than m, a particle is called ultrarelativistic. In this limit Ẽ → ∞ and ˜L → ∞while the ratio ˜L /Ẽ remains finite and is equal to ˜b := b/rS, where b is the impact parameter of the particle at infinity. The equations of motion of the ultrarelativistic particle (or a light ray) take the form (˜t = t/rS):
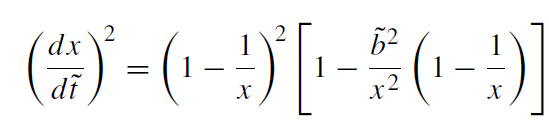 (1.1)
(1.1)
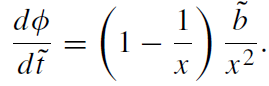 (1.2)
(1.2)
The sign of b depends on the sense of motion; we assume that b is positive. The radial turning point on the trajectory is defined by the equation
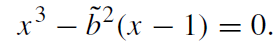 (1.3)
(1.3)
The impact parameter b as a function of the position of a radial turning point is shown in figure 1.1.
1.2 Types of trajectory
In figure 1.1, the motion of an ultrarelativistic particle with a given b is represented by a horizontal line b = constant. A particle approaches the black hole,
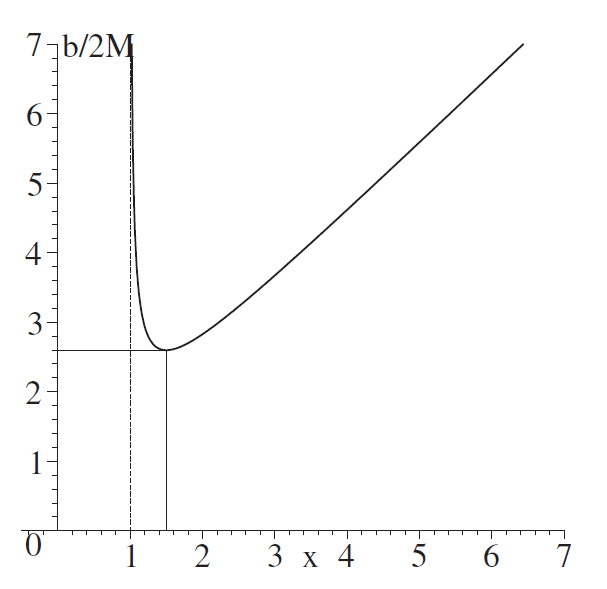
Figure 1.1. Impact parameter b as a function of the position of extrema in x = r/rS on the trajectory of an ultrarelativistic particle.
passes by it at the minimal distance corresponding to the point of intersection of b = constant with the right-hand branch of the b(r ) curve, and again recedes to infinity. If the intersection occurs close to the minimum bmin = 3√3 × rS/2, the particle may experience a number of turns before it flies away to infinity. The exact minimum of the curve b(r) corresponds to the (unstable) motion on a circle of radius r = 1.5rS at the velocity v = c. Note that the left-hand branch of b(r) in figure 1.1 corresponds to the maximum distance between the ultrarelativistic particle and the black hole; the particle first recedes to r < 1.5rS but then again falls into the black hole. Obviously, for such a motion the parameter b does not have the literal meaning of the impact parameter at infinity since the particle never recedes to infinity. For a given coordinate r , this parameter can be found as a function of the angle ψ between the trajectory of the particle and the direction to the center of the black hole:
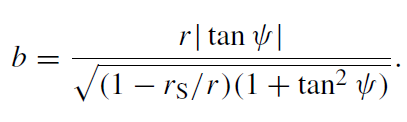 (1.4)
(1.4)
If an ultrarelativistic particle approaches the black hole on the way from infinity and the parameter b is less than the critical value bmin = 3√3rS/2, the particle falls into the black hole.
 الاكثر قراءة في الثقوب السوداء
الاكثر قراءة في الثقوب السوداء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















