

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Dioxygen
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 437
11-3-2017
2290
Dioxygen
Dioxygen is obtained industrially by the liquefaction and fractional distillation of air, and is stored and transported as a liquid. Convenient laboratory preparations of O2 are the electrolysis of aqueous alkali using Ni electrodes, and decomposition of H2O2 (equation 1.1). A mixture of KClO3 and MnO2 used to be sold as ‘oxygen mixture’ (equation 1.2) and the thermal decompositions of many other oxo salts (e.g. KNO3, KMnO4 and K2S2O8) produce O2.
 ) 1.1(
) 1.1(
 (1.2(
(1.2(
Dioxygen is a colourless gas, but condenses to a pale blue liquid or solid. and 1.13. In all phases, it is paramagnetic with a triplet ground state, i.e. the two unpaired electrons have the same spin, with the valence electron configuration being:
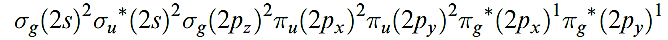
In this state, O2 is a powerful oxidizing agent but, fortunately, the kinetic barrier is often high; if it were not, almost all organic chemistry would have to carried out in closed systems. However, asinglet state, O2- , with a valence electron configuration of:
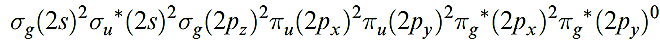
lies only 95 kJ mol-1 above the ground state. This excited state can be generated photochemically by irradiation of O2 in the presence of an organic dye as sensitizer, or nonphotochemically by reactions such as 1.3.
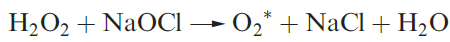 (1.3)
(1.3)
Singlet O2 is short-lived, but extremely reactive, combining with many organic compounds, e.g. in reaction 1.4, O2- acts as a dienophile in a Diels–Alder reaction.
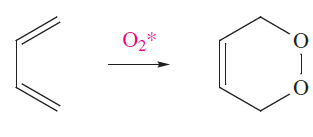 (1.4)
(1.4)
At high temperatures, O2 combines with most elements, exceptions being the halogens and noble gases, and N2 unless under special conditions. Reactions with the group 1 metals are of particular interest, oxides, peroxides, superoxides and suboxides being possible products. Bond lengths in O2, [O2]- and [O2]2- are 121, 134 and 149pm , consistent with a weakening of the bond caused by increased occupation of the π* MOs. The first ionization energy of O2 is 1168 kJ mol-1 and it may be oxidized by very powerful oxidizing agents such as PtF6 (equation 1.5). The bond distance of 112pm in [O2]+ is in keeping with the trend for O2, [O2]- and [O2]2-. Other salts include [O2]+[SbF6]- (made from irradiation of O2 and F2 in the presence of SbF5, or from O2F2 and SbF5) and [O2]+[BF4]- (equation 1.6).
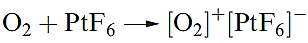 (1.5)
(1.5)
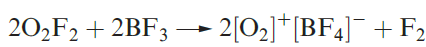 (1.6)
(1.6)
The chemistry of O2 is an enormous topic, and examples of its reactions can be found throughout this book.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















