
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Imperfections in Solids
المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
الجزء والصفحة:
p 13
8-5-2017
1956
Imperfections in Solids
One type of imperfection that all crystals have in common is atomic thermal vibration. A perfect single crystal contains atoms at particular lattice sites, the atoms separated from each other by a distance we have assumed to be constant. The atoms in a
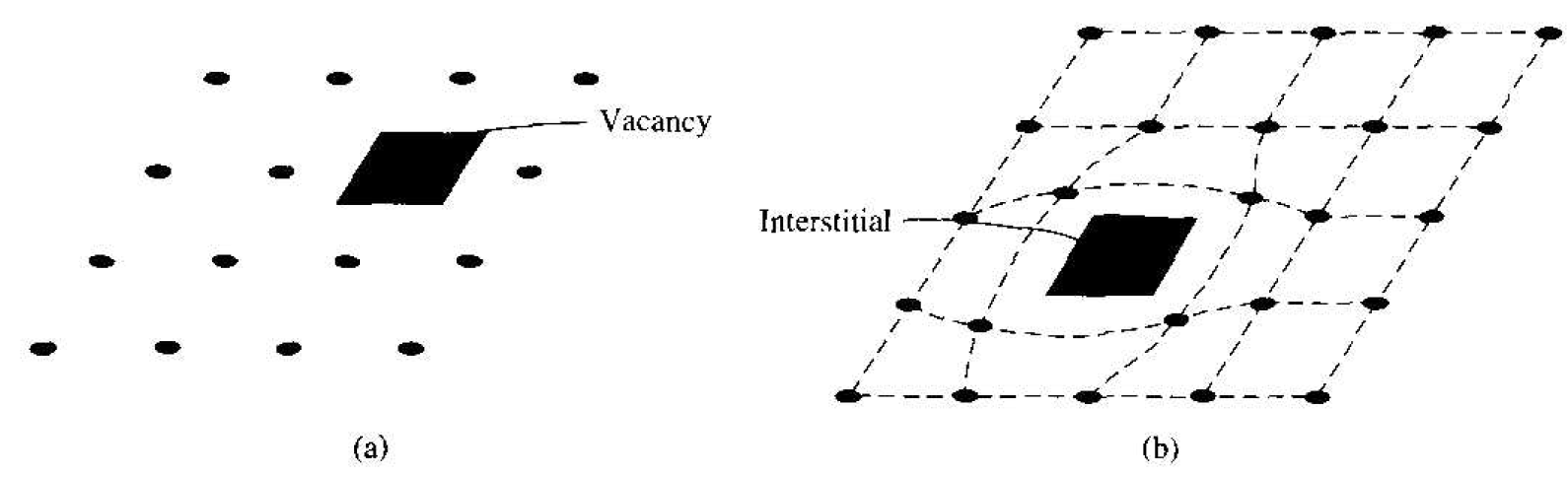
Figure 1.1 Two-dimensional representation of a single-crystal lattice showing (a) a vacancy defect and (b) an interstitial defect.
crystal, however, have a certain thermal energy, which is a function of temperature. The thermal energy causes the atoms to vibrate in a random manner about an equilibrium lattice point. This random thermal motion causes the distance between atoms to randomly fluctuate, slightly disrupting the perfect geometric arrangement of atoms. This imperfection, called lattice vibrations, affects some electrical parameters, as we will see later in our discussion of semiconductor material characteristics.
Another type of defect is called a point defect. There are several of this type that we need to consider. Again, in an ideal single-crystal lattice, the atoms are arranged in a perfect periodic arrangement. However, in a real crystal, an atom may be missing from a particular lattice site. This defect is referred to as a vacancy: it is schematically shown in Figure 1.1a. In another situation, an atom may be located between lattice sites. This defect is referred to as an interstitial and is schematically shown in Figure 1.1b. In the case of vacancy and interstitial defects, not only is the perfect geometric arrangement of atoms broken, but also the ideal chemical bonding between atoms is disrupted, which tends to change the electrical properties of the material. A vacancy and interstitial may be in close enough proximity to exhibit an interaction between the two point defects. This vacancy-interstitial defect, also known as a Frenkel defect, produces different effects than the simple vacancy or interstitial.
The point defects involve single atoms or single-atom locations. In forming single-crystal materials, more complex defects may occur. A line defect. for example, occurs when an entire row of atoms is missing from its normal lattice site. This defect is referred to as a line dislocation and is shown in Figure 1.2. As with a point defect, a line dislocation disrupts both the normal geometric periodicity of the lattice and the ideal atomic bonds in the crystal. This dislocation can also alter the electrical properties of the material, usually in a more unpredictable manner than the simple point defects.
Other complex dislocations can also occur in it crystal lattice. However, this introductory discussion is intended only to present a few of the basic types of defect, and to show that a real crystal is not necessarily a perfect lattice structure. The effect of these imperfections on the electrical properties of a semiconductor will be considered in later chapters.
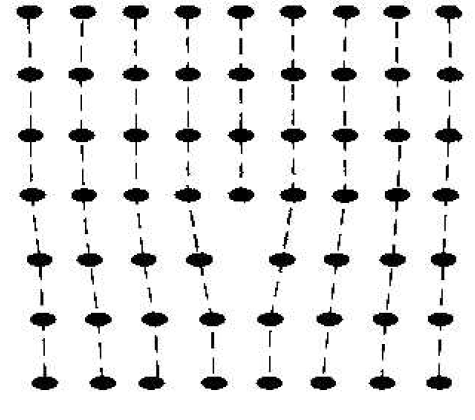
Figure 1.2 A two dimensional representation of a line dislocation.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















