
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء والفلسفة

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Primitive and Unit Cell
المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
الجزء والصفحة:
p 3
8-5-2017
4268
Primitive and Unit Cell
We can represent a particular atomic array by a dot that is called a lattice point. Figure 1.1 shows an infinite two-dimensional array of lattice points. The simplest means of repeating an atomic array is by translation. Each lattice point in Figure 1.1 can be translated a distance a1 in one direction and a distance b1 in a second non-colinear direction to generate the two-dimensional lattice. A third non-colinear translation will produce the three-dimensional lattice. The translation directions need not be perpendicular.
Since the three-dimensional lattice is a periodic repetition of a group of atoms, we do not need to consider the entire lattice, but only a fundamental unit that is being repeated. A unit cell is a small volume of the crystal that can be used to reproduce the entire crystal. A unit cell is not a unique entity. Figure 1.2 shows several possible unit cells in a two-dimensional lattice.
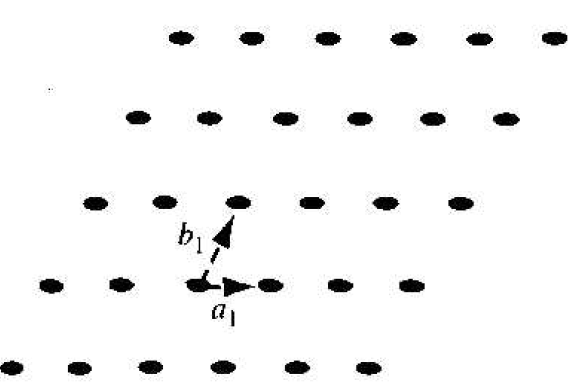
Figure 1.1 Two-dimensional representation of a single-crystal lattice.
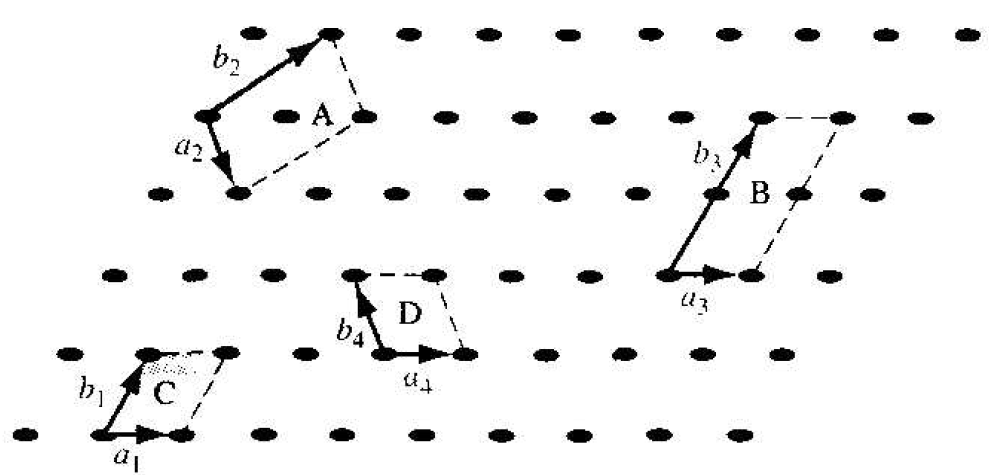
Figure 1.2 Two-dimensional representation of a single-crystal lattice showing various possible unit cells.

Figure 1.3 A generalized primitive unit cell.
The unit cell A can be translated in directions a2 and b2, the unit cell B can be translated in directions a3 and b3, and the entire two-dimensional lattice can be constructed by the translations of either of these unit cells. The unit cells C and D in Figure 1.2 can also be used to construct the entire lattice by using the appropriate translations. This discussion of two-dimensional unit cells can easily be extended to three dimensions to describe a real single-crystal material.
A primitive cell is the smallest unit cell that can be repeated to form the lattice. In many cases, it is more convenient to use a unit cell that is not a primitive cell. Unit cells may be chosen that have orthogonal sides, thr example, whereas the sides of a primitive cell may be non-orthogonal.
A generalized three-dimensional unit cell is shown in Figure 1.3. The relationship between this cell and the lattice is characterized by three vectors 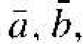 and
and 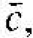 which need not be perpendicular and which may or may not be equal in length. Every equivalent lattice point in the three-dimensional crystal can be found using the vector
which need not be perpendicular and which may or may not be equal in length. Every equivalent lattice point in the three-dimensional crystal can be found using the vector
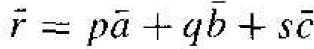 (1)
(1)
where p, q, and s are integers. Since the location of the origin is arbitrary, we will let p. q, and s be positive integers for simplicity.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















