
The Diamond Structure
 المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
 المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 9
الجزء والصفحة:
p 9
 8-5-2017
8-5-2017
 2131
2131
The Diamond Structure
As already stated, silicon is the most common semiconductor material. Silicon is referred to as a group IV element and has a diamond crystal structure. Germanium is also a group 1V element and has the same diamond structure. A unit cell of the diamond structure, shown in Figure 1.1, is more complicated than the simple cubic structures that we have considered up to this point.
We may begin to understand the diamond lattice by considering the tetrahedral structure shown in Figure 1.2. This structure is basically a body-centered cubic with
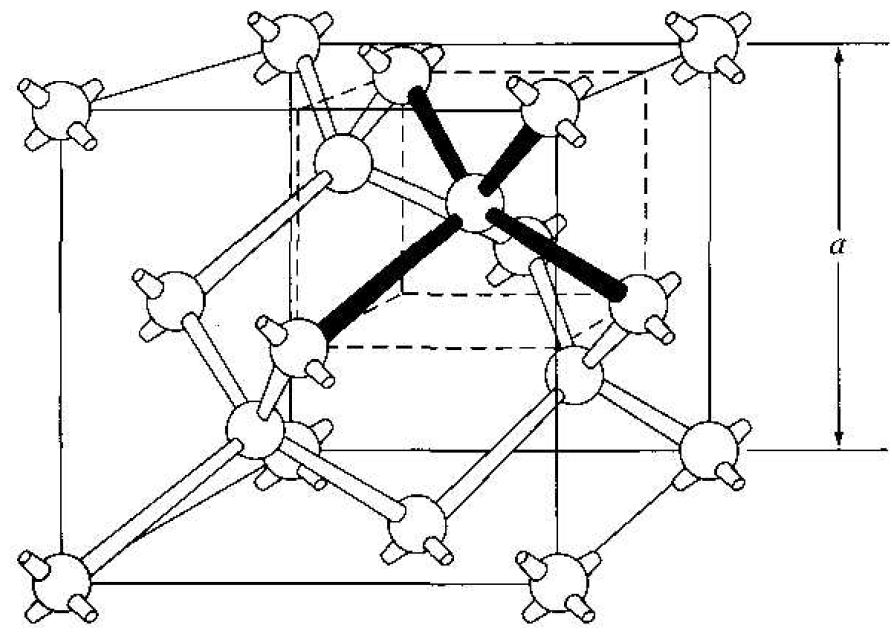
Figure 1.1 The diamond structure.
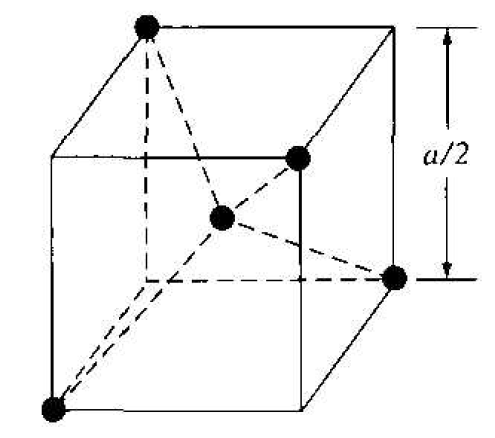
Figure 1.2 The tetrahedral structure of closest neighbors in the diamond lattice.
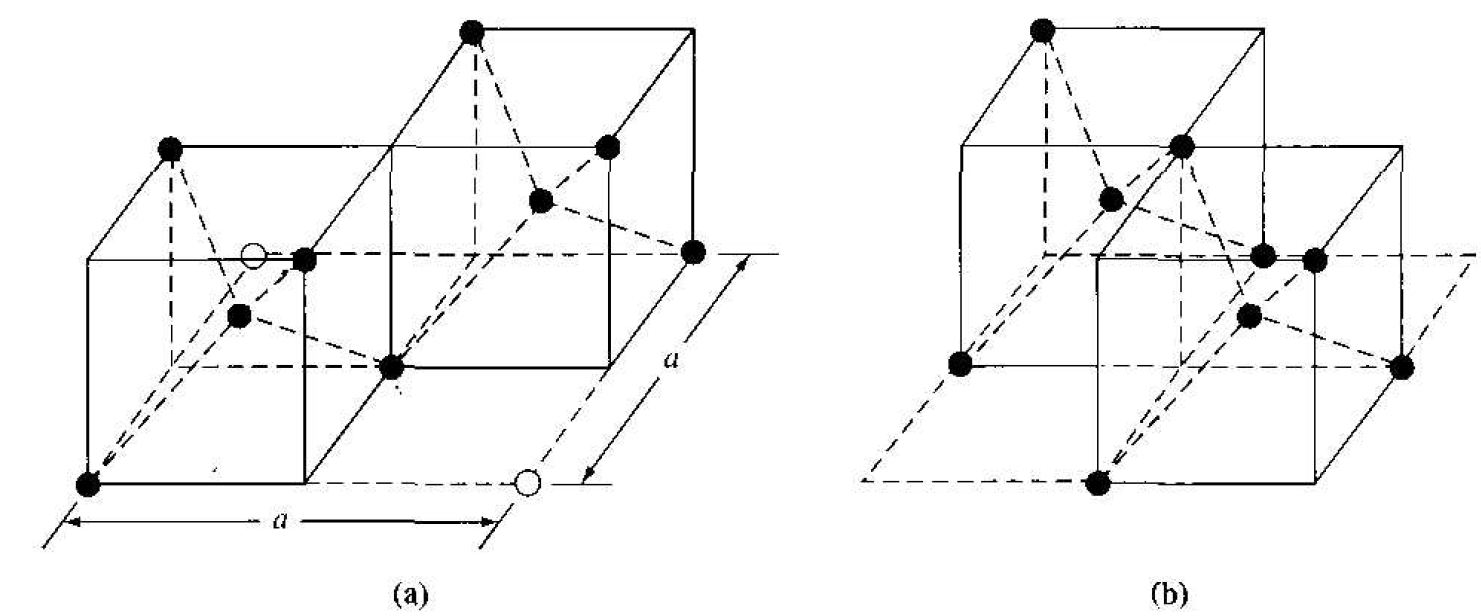
Figure 1.3 Portions of the diamond lattice: (a) bottom half and (b) top half.
four of the comer atoms missing. Every atom in the tetrahedral structure has four nearest neighbors and it is this structure which is the basic building block of the diamond lattice.
There are several ways to visualize the diamond structure. One way to gain a further understanding of the diamond lattice is by considering Figure l . 3. Figure l . 3a shows two body-centered cubic, or tetrahedral, structures diagonally adjacent to each other. The shaded circles represent atoms in the lattice that are generated when the structure is translated to the right or left, one lattice constant, a. Figure 1.3b represents the top half of the diamond structure. The top half again consists of two tetrahedral structures joined diagonally, but which are at 90o with respect to the bottom half diagonal. An important characteristic of the diamond lattice is that any atom within the diamond structure will have four nearest neighboring atoms. We will note this characteristic again in our discussion of atomic bonding in the next section.
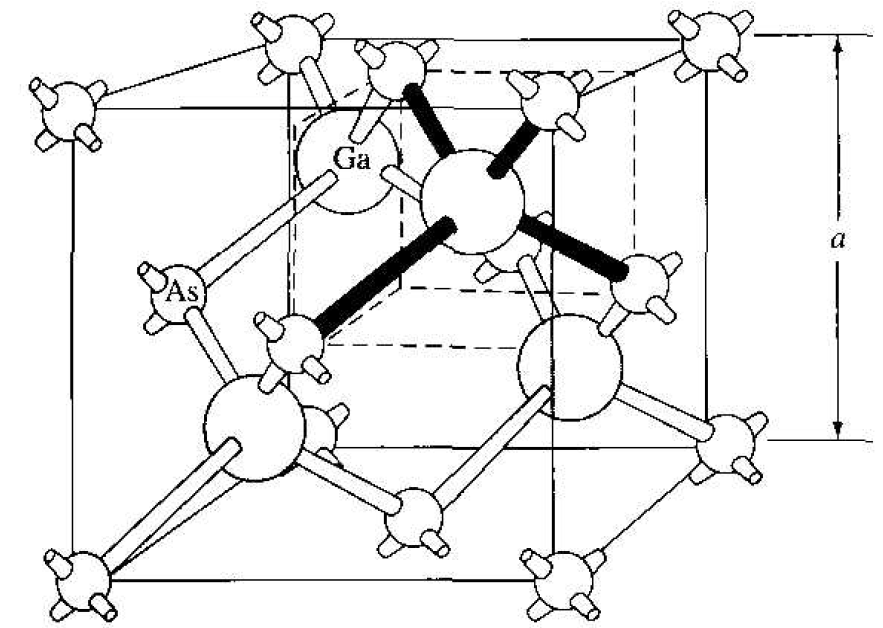
Figure 1.4 The zincblende (sphalerite) lattice of GaAs.
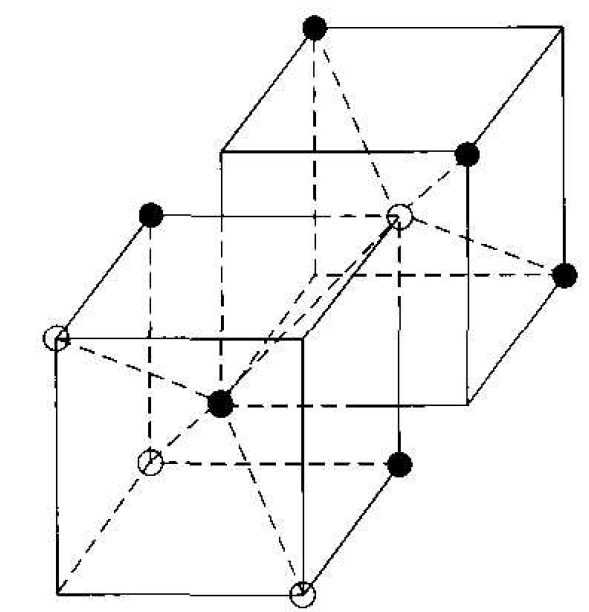
Figure 1.5 The tetrahedral structure of closest neighbors in the zincblende lattice.
The diamond structure refers to the particular lattice in which all atoms are of the same species, such as silicon or germanium. The zincblende (sphalerite) structure differs from the diamond structure only in that there are two different types of atoms in the lattice. Compound semiconductors, such as gallium arsenide, have the zincblende structure shown in Figure 1.4. The important feature of both the diamond and the zincblende structures is that the atoms art: joined together to form a tetrahedron. Figure 1.5 shows the basic tetrahedral structure of GaAs in which each Ga atom has four nearest As neighbors and each As atom has four nearest Ga neighbors. This figure also begins to show the interpenetration of two sublattices that can be used to generate the diamond or zincblende lattice.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


