

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The Chiral Drug Thalidomide
المؤلف:
John McMurry
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
9th. p 182
16-5-2017
1858
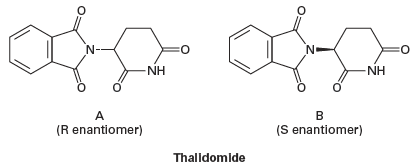
The Chiral Drug Thalidomide
In the late 1950s, thalidomide was a drug marketed to treat morning sickness in pregnant women and also prescribed as a sedative. Shortly thereafter, the drug was found to cause birth defects, namely phocomelia (malformation of the limbs) in infants. Some 10,000 cases of phocomelia had surfaced by the time thalidomide use was halted; about half the afflicted children survived past infancy.
The drug was marketed as a racemic mixture of two isomers (A and B). (R)-Thalidomide (isomer A) has sedative and antiemetic (anti-nausea) effects, whereas the S enantiomer (isomer B) is a teratogen. The enantiomers can interconvert in vivo—that is, if a human is given pure (R)-thalidomide or (S)-thalidomide, both isomers can be found in the serum—therefore, administering only one enantiomer will not prevent the teratogenic effect in humans.
The S isomer was found to insert (intercalate) into subunits of DNA, mainly by attachments to guanine, thus interrupting normal development. The negative impact of this drug on the general public resulted in more rigorous assessment of drugs in development. Now, all regulatory bodies demand an examination of isomeric purity as well as clinical and toxicity testing before approval of a new drug.
The teratogenic mechanism of the S isomer results in an interference with the production of certain proteins necessary for angiogenesis, the process whereby new blood vessels are formed. A lack of blood vessels deprives a growing limb of critical nutrients, resulting in stunted growth. Medicinal chemists have realized that angiogenesis is crucial for the development of malignant tumors and thus have investigated thalidomide as a therapeutic agent against certain cancers. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has now approved thalidomide for use in newly diagnosed cases of multiple myeloma.
The teratogenic mechanism of the S isomer results in an interference with the production of certain proteins necessary for angiogenesis, the process whereby new blood vessels are formed. A lack of blood vessels deprives a growing limb of critical nutrients, resulting in stunted growth. Medicinal chemists have realized that angiogenesis is crucial for the development of malignant tumors and thus have investigated thalidomide as a therapeutic agent against certain cancers. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has now approved thalidomide for use in newly diagnosed cases of multiple myeloma.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















