

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Alkylation of Acetylide Anions
المؤلف:
John McMurry
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
9th. p 277
24-5-2017
5579
Alkylation of Acetylide Anions
The negative charge and unshared electron pair on carbon make an acetylide anion strongly nucleophilic. As a result, an acetylide anion can react with electrophiles, such as alkyl halides, in a process that replaces the halide and yields a new alkyne product.
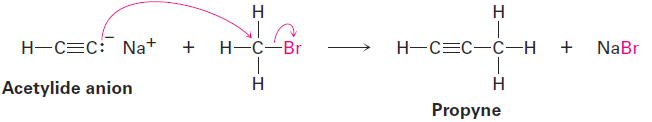
We won’t study the details of this substitution reaction but for now you can picture it as happening by the pathway shown in Figure 1.1. The nucleophilic acetylide ion uses an electron pair to form a bond to the positively polarized, electrophilic carbon atom of bromomethane. As the new C - C bond forms, Br- departs, taking with it the electron pair from the former C - Br bond and yielding propyne as product. We call such a reaction an alkylation because a new alkyl group has become attached to the starting alkyne.
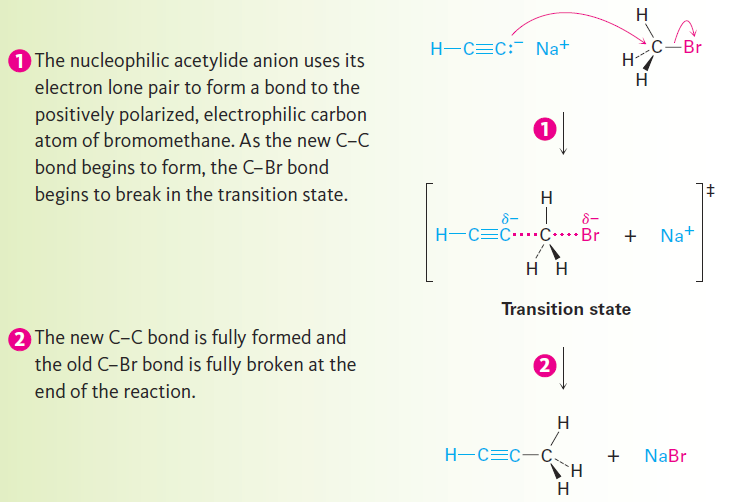
Figure 1.1: A mechanism for the alkylation reaction of acetylide anion with bromomethane to give propyne.
Alkyne alkylation is not limited to acetylene itself. Any terminal alkyne can be converted into its corresponding anion and then allowed to react with an alkyl halide to give an internal alkyne product. Hex-1-yne, for instance, gives dec-5-yne when treated first with NaNH2 and then with 1-bromobutane.
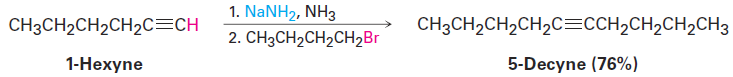
Because of its generality, acetylide alkylation is a good method for preparing substituted alkynes from simpler precursors. A terminal alkyne can be prepared by alkylation of acetylene itself, and an internal alkyne can be prepared by further alkylation of a terminal alkyne.
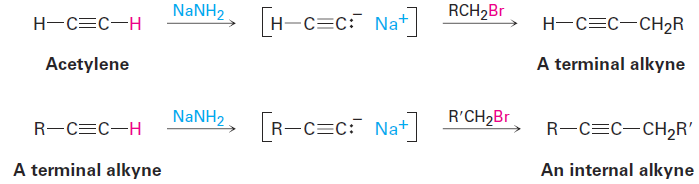
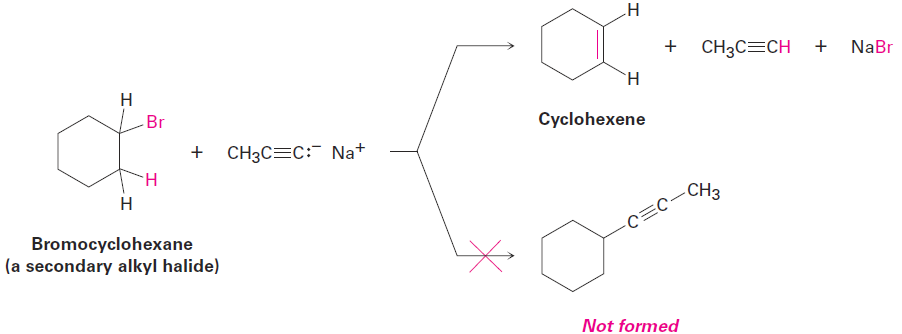
The alkylation reaction can only use primary alkyl bromides and alkyl iodides because acetylide ions are sufficiently strong bases to cause elimination instead of substitution when they react with secondary and tertiary alkyl halides. For example, reaction of bromocyclohexane with propyne anion yields the elimination product cyclohexene rather than the substitution product 1-propynylcyclohexane.
 الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















