


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 9-5-2016
Date: 3-7-2019
Date: 8-8-2017
|
Isomerization Process
Isomerization is a small-volume but important refinery process. Like alkylation, it is acid catalyzed and intended to produce highly-branched hydrocarbon mixtures. The low octane C5/C6 fraction obtained from natural gasoline or from a light naphtha fraction may be isomerized to a high octane product.
Dual-function catalysts activated by either inorganic or organic chlorides are the preferred isomerization catalysts. A typical catalyst is platinum with a zeolite base. These catalysts serve the dual purpose of promoting carbonium ion formation and hydrogenation-dehydrogenation reactions. The reaction may start by forming a carbocation via abstraction of a hydride ion by a catalyst acid site. Alternatively, an olefin formed on the catalyst surface could be protonated to form the carbocation.
The carbocation isomerizes by a 1,2-hydride/methide shift as mentioned earlier (see this chapter, “Reforming Reactions”). Figure 1.1 shows the vapor phase equilibrium of hexane isomers.
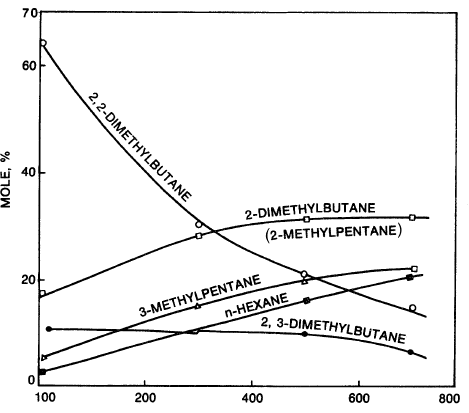
Figure 1.1. Vapor phase equilibrium for hexanes.



|
|
|
|
دراسة: حفنة من الجوز يوميا تحميك من سرطان القولون
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تنشيط أول مفاعل ملح منصهر يستعمل الثوريوم في العالم.. سباق "الأرنب والسلحفاة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الطلبة المشاركون: مسابقة فنِّ الخطابة تمثل فرصة للتنافس الإبداعي وتنمية المهارات
|
|
|