
Production of Methanol
 المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
 المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 150
الجزء والصفحة:
p 150
 13-8-2017
13-8-2017
 1950
1950
Production of Methanol
Methanol is produced by the catalytic reaction of carbon monoxide and hydrogen (synthesis gas). Because the ratio of CO:H2 in synthesis gas from natural gas is approximately 1:3, and the stoichiometric ratio required for methanol synthesis is 1:2, carbon dioxide is added to reduce the surplus hydrogen. An energy-efficient alternative to adjusting the CO:H2 ratio is to combine the steam reforming process with autothermal reforming (combined reforming) so that the amount of natural gas fed is that required to produce a synthesis gas with a stoichiometric ratio of approximately 1:2.05. Figure 5-4 is a combined reforming diagram.
If an autothermal reforming step is added, pure oxygen should be used. (This is a major difference between secondary reforming in case of ammonia production, where air is used to supply the needed nitrogen).


Figure 5-4. A block flow diagram showing the combined reforming for methanol synthesis.
An added advantage of combined reforming is the decrease in NOx emission. However, a capital cost increase (for air separation unit) of roughly 15% is anticipated when using combined reforming in comparison to plants using a single train steam reformer. The process scheme is viable and is commercially proven. The following reactions are representative for methanol synthesis.


Old processes use a zinc-chromium oxide catalyst at a high-pressure range of approximately 270–420 atmospheres for methanol production. A low-pressure process has been developed by ICI operating at about 50 atm (700 psi) using a new active copper-based catalyst at 240°C. The synthesis reaction occurs over a bed of heterogeneous catalyst arranged in either sequential adiabatic beds or placed within heat transfer tubes.
The reaction is limited by equilibrium, and methanol concentration at the converter’s exit rarely exceeds 7%. The converter effluent is cooled to 40°C to condense product methanol, and the unreacted gases are recycled. Crude methanol from the separator contains water and low levels of by-products, which are removed using a two-column distillation system. Figure 1.1 shows the ICI methanol synthesis process.

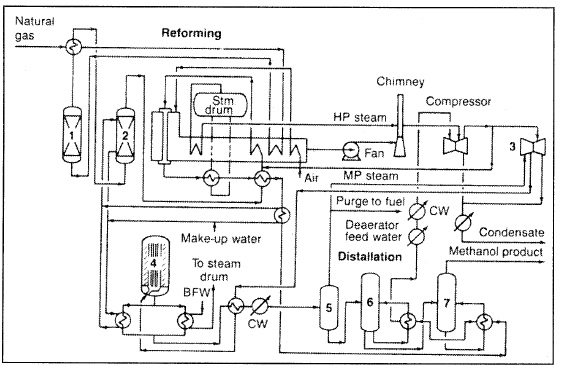
Figure 1.1. The ICI low-pressure process for producing methanol: (1) desulfurization, (2) saturator (for producing process steam), (3) synthesis loop circulator, (4) reactor, (5) heat exchanger and separator, (6) column for light ends recovery, (7) column for water removal.
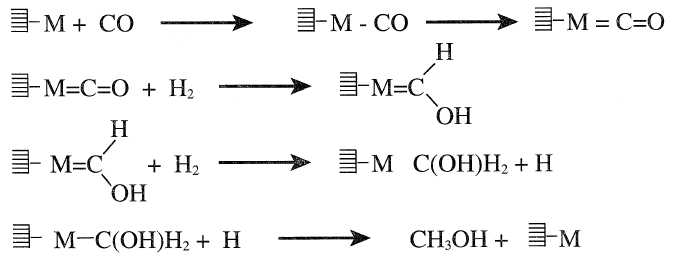
Methanol synthesis over the heterogeneous catalyst is thought to occur by a successive hydrogenation of chemisorbed carbon monoxide.
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


