

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
THE TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION
المؤلف:
James R Hanson
المصدر:
Chemistry and Medicines
الجزء والصفحة:
p 66
9-10-2017
1642
THE TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION
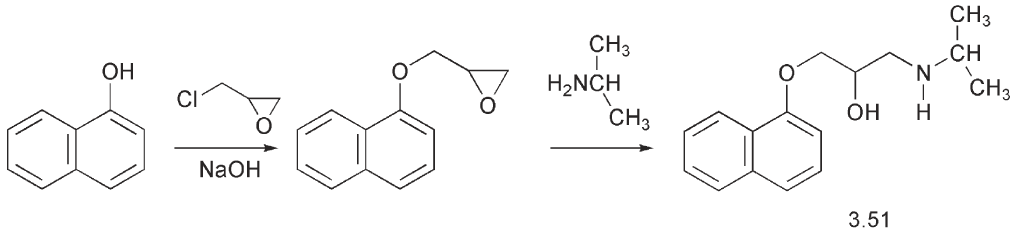
There are other approaches to the treatment of hypertension arising from the heart muscle having to pump too hard. The adrenergic receptors are associated with ligand-gated ion-channels. Opening these channels allows an influx of calcium ions into the cell. This leads to the formation of a complex between the calcium ion and an intracellular protein, calmodulin, which then initiates muscle contraction. Compounds that block the opening of these ion-channels can have a vasodilating effect and are then useful in the treatment of hypertension. A number of dihydropyridines introduced in the 1970s such as nifedipine 3.55, have this action. Although nifedipine can be made by the classical
Hantzsch synthesis using 2-nitrobenzaldehyde, ethyl acetoacetate and ammonia, a cleaner product is obtained by a two-step reaction. 2- Nitrobenzaldehyde is condensed with one mole of ethyl acetoacetate to give the benzylidene derivative 3.56. Addition of the enamine, ethyl 3- aminocrotonate 3.57, then gives nifedipine 3.55. Another useful drug, which appears to act as a calcium channel blocking agent is verapamil 3.58. The more active isomer is the 2S-(-)-verapamil.
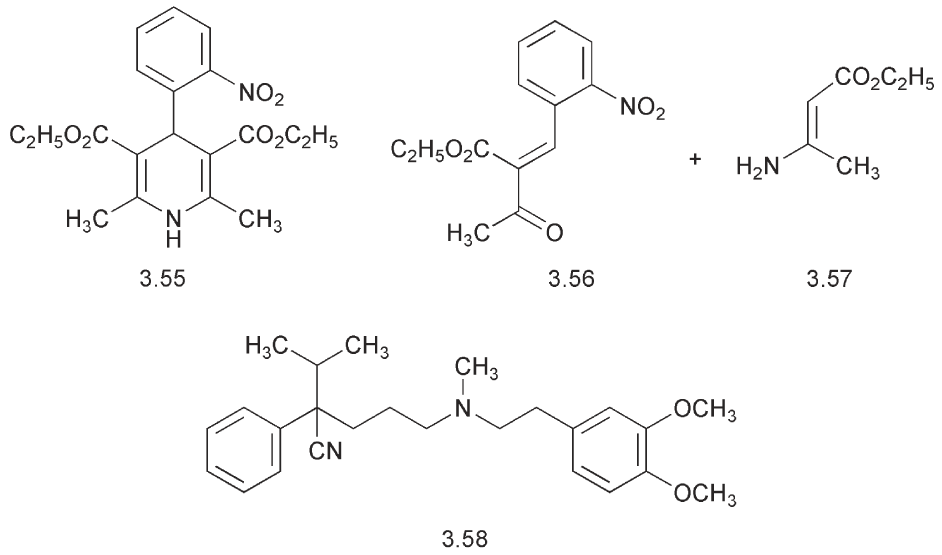
High blood pressure, hypertension, can be controlled by β-blockers, by calcium channel blockers or by increasing water excretion with diuretics that act on the kidneys. Compounds that are diuretics can have side effects arising from alteration of the electrolyte balance. A further method is to restrict the formation of the peptide hormone, angiotensin II, which activates receptors located in the smooth muscle of the arterioles that bring about vasoconstriction. Many peptide hormones are formed by the cleavage of longer peptide chains. Angiotensin
II is an octapeptide, which is produced as part of the renin–angiotensin cascade (see Scheme 1). Inhibition of the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) by which a decapeptide angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II provides a means of achieving this. The ACE is a carboxydipeptidase, which cleaves angiotensin I between a phenylalanine and a histidine two residues from the C-terminus of the peptide. This enzyme system has a zinc ion at the active site. Captopril 3.59 was designed as a substratemimic containing an appropriately placed thiol group to bind to the zinc. The synthesis of captopril has to generate the correct absolute stereochemistry. One way in which this was achieved was by the microbiological hydration of methacrylic acid.
The ACE is a relatively non-specific protease and has a number of other substrates and consequently the inhibition can lead to side effects. Another approach to controlling hypertension is to block the angiotensin II receptors. Losarten 3.60 is an effective drug for this purpose. Although at first sight the structure would appear to impose some synthetic difficulties, a convergent synthesis has provided structural flexibility to allow structure:activity relationships to be established. The use of a tetrazole as an acid mimic to impart solubility is an interesting structural feature.
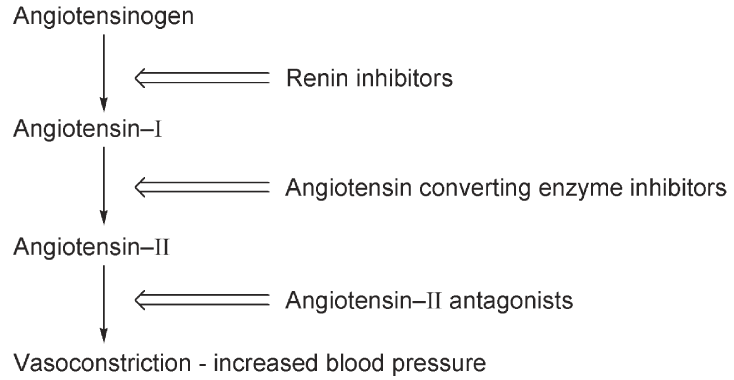
Scheme 1 The angiotensin–renin cascade
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















