
Molecular Elements
 المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
 المصدر:
................
المصدر:
................
 الجزء والصفحة:
.................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
 27-7-2020
27-7-2020
 1549
1549
Molecular Elements
There are many substances that exist as two or more atoms connected together so strongly that they behave as a single particle. These multi-atom combinations are called molecules. The smallest part of a substance that has the physical and chemical properties of that substance. A molecule is the smallest part of a substance that has the physical and chemical properties of that substance. In some respects, a molecule is similar to an atom. A molecule, however, is composed of more than one atom.
Table 1 : Elements That Exist as Diatomic Molecules
| Hydrogen, H |
Oxygen |
Nitrogen |
Fluorine |
Chlorine |
Bromine |
Iodine |
Some elements exist naturally as molecules. For example, hydrogen and oxygen exist as two-atom molecules. Other elements also exist naturally as diatomic molecules. A molecule with only two atoms (Table 1 ). As with any molecule, these elements are labeled with a molecular formula, a formal listing of what and how many atoms are in a molecule. (Sometimes only the word formula is used, and its meaning is inferred from the context.) For example, the molecular formula for elemental hydrogen is H2, with H being the symbol for hydrogen and the subscript 2 implying that there are two atoms of this element in the molecule. Other diatomic elements have similar formulas: O2, N2, and so forth. Other elements exist as molecules—for example, sulfur normally exists as an eight-atom molecule, S8, while phosphorus exists as a four-atom molecule, P4 (Figure 1).
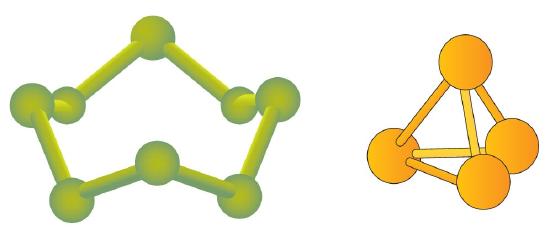
Figure 1 : Molecular Art of S8 and P4 Molecules. If each green ball represents a sulfur atom, then the diagram on the left represents an S8 molecule. The molecule on the right shows that one form of elemental phosphorus exists, as a four-atom molecule.
Figure 1 shows two examples of how we will be representing molecules in this text. An atom is represented by a small ball or sphere, which generally indicates where the nucleus is in the molecule. A cylindrical line connecting the balls represents the connection between the atoms that make this collection of atoms a molecule. This connection is called a chemical bond.
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء عامة
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء عامة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


